ch hdg (prev pt 1 hdg) sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 3
This regulation may be cited as the Plant Protection Regulation 2002 .
This regulation commences on 1 September 2002.
The dictionary in schedule 13 defines particular words used in this regulation.
ch hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 4
pt hdg (prev pt 2 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 5
Each organism, virus, viroid, disorder, condition or cause of specified symptoms in plants mentioned in schedule 1 is prescribed for section 4 (1) of the Act.
5References to prescribed pests
(1)If a prescribed pest has a life cycle, a reference in this regulation to the pest includes a reference to the pest at each stage of the pest’s life cycle.Examples of stages of the pest’s life cycle—
egg, larva, pupa, adult(2)If schedule 1 states an abbreviated or common name for a prescribed pest, the body of this regulation refers to the pest by that name.
Each pest mentioned in schedule 2 is declared to be a notifiable pest for section 12 (1) of the Act.
pt hdg (prev pt 2A hdg) ins 2006 SL No. 179 s 3
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 5
6ADeclared class for appointment—Act, s 6D
For section 6D (2) (a) (ii) of the Act, the class of individual declared to be an approved class is an individual employed by—(a)BSES Ltd ACN 103 760 005; or(b)Queensland Cane Growers Organisation Ltd ACN 089 992 969; or(c)Isis Productivity Ltd ACN 108 518 216; or(d)a mill owner under the Sugar Industry Act 1999 ; or(e)an entity engaged in sugarcane production in Queensland; or(f)an entity whose objects include improving sugar industry production.s 6A ins 2006 SL No. 179 s 3
7Sale of infested plant prohibited
A person must not, in trade or commerce, sell or dispose of, or possess for sale, a plant the person knows is, or reasonably believes may be, infested with a prescribed pest.Maximum penalty—20 penalty units.
A person must not possess a plant introduced into Queensland in trade or commerce unless—(a)the plant is identified as to the place where it was grown or despatched; and(b)if the plant is in a package, a clear and legible description of the contents of the package is clearly marked on the package together with the name and address of both the sender and the recipient.Maximum penalty—20 penalty units.
s 8 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 3
9Certification of disinfestation
(1)If an inspector gives a direction under section 13 of the Act to a person to disinfest a plant, the person must disinfest the plant within 72 hours before introducing or moving the plant.Maximum penalty—20 penalty units.
(2)If the plant is disinfested under the inspector’s direction, the inspector must, if the recipient of the plant requests, give the recipient a certificate to that effect.
10Plant to be repacked if certificate given
A person must, within 24 hours of receiving a certificate issued under section 9, repack and remove the plant from the place of treatment.Maximum penalty—20 penalty units.
A person must not sell a grafted citrus fruit tree unless it is of upright growth with the stock-scion union at least 100mm above the point where the first lateral root branches from the main stem.Maximum penalty—20 penalty units.
pt hdg sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 6
12Declaration of corresponding laws
For the definition corresponding law in schedule 2 of the Act, each of the following is declared to be a corresponding law to the Act—(a) Plant Health Act 2009 (SA);(b) Plant Diseases Act 1914 (WA);(c) Plant Diseases Act 1924 (NSW);(d) Plant Diseases Act 2002 (ACT);(e) Plant Diseases Control Act (NT);(f) Plant Health and Plant Products Act 1995 (Vic);(g) Plant Quarantine Act 1997 (Tas).s 12 sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 6
amd SL No. 202 s 3
pt hdg ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 3
13Use of agricultural chemical products
This regulation does not authorise the use of an agricultural chemical product within the meaning of the Chemical Usage (Agricultural and Veterinary) Control Act 1988 , schedule, other than in a way authorised under that Act.s 13 prev s 13 om 2006 SL No. 234 s 6
pres s 13 ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 3
s 14 om 2006 SL No. 234 s 6
s 15 om 2006 SL No. 234 s 6
s 16 om 2006 SL No. 234 s 6
ch hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 7
pt hdg (prev pt 5 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
In this part—banana freckle means freckle disease of banana, associated with either of the following genera of fungi that are pathogenic to plants or bananas—(a) Guignardia spp.;(b) Phyllosticta spp., other than Phyllosticta maculata M.H. Wong & Crous.def banana freckle ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 3 (2)
banana plant—(a)generally, means a plant of the genera Musa or Ensete; and(b)for division 3, see also section 20.banana plant pest ...def banana plant pest om 2013 SL No. 193 s 3 (1)
ground cover vegetation means any low spreading plant that covers the soil and retards movement of soil.other thing includes clothing, footwear, packaging material and banana bunch covers, but does not include fruit of a banana plant.def other thing ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 3 (2)
pest banana plant means a plant of the genera—(a) Musa spp., other than—(i)a plant that produces edible fruit; or(ii)an indigenous plant that is not a volunteer plant; or(b) Ensete spp.def pest banana plant amd 2009 SL No. 149 s 3
pest quarantine area means—(a)for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle—each of the pest quarantine areas declared under section 18; or(b)for tropical race 4—the pest quarantine area declared under section 19A; or(c)for banana freckle—the pest quarantine area declared under section 19C.def pest quarantine area sub 2013 SL No. 32 s 3; 2013 SL No. 193 s 3
pest site see section 25.treatment method A see schedule 5, item 1.treatment method B see schedule 5, item 2.treatment method C see schedule 5, item 3.treatment method D see schedule 5, item 4.tropical race 4 means fusarium wilt of banana, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Fusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f. sp. cubense (E.F. Smith) W.C. Snyder and H.N. Hansen, tropical race 4.def tropical race 4 ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 3 (2)
s 17 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
sdiv hdg ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 4
amd 2013 SL No. 193 s 4
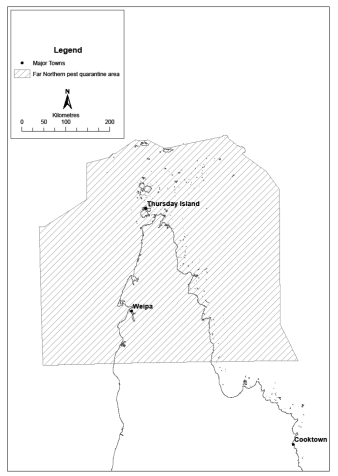
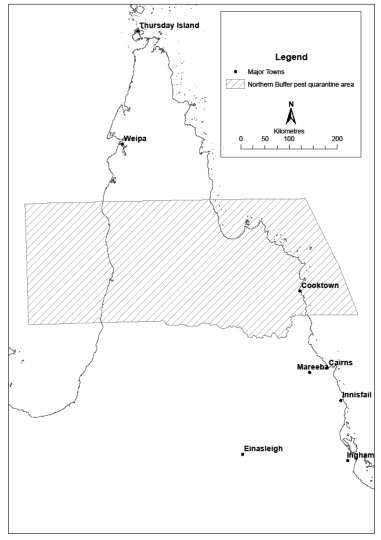
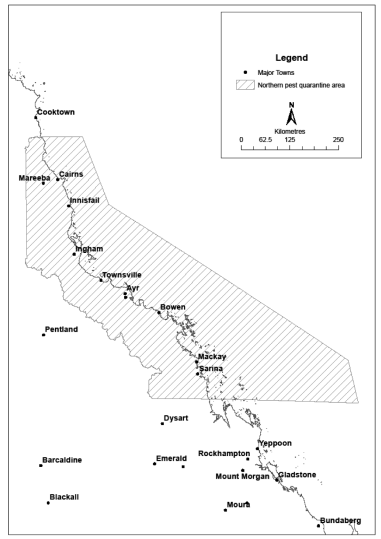
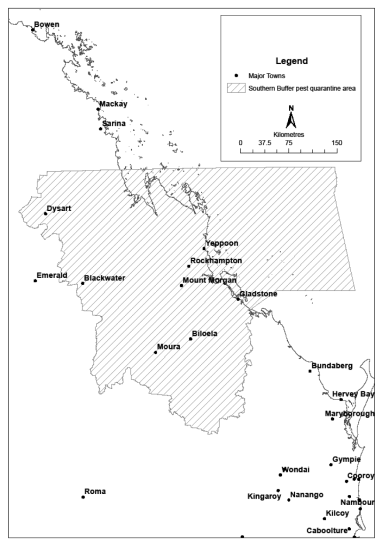
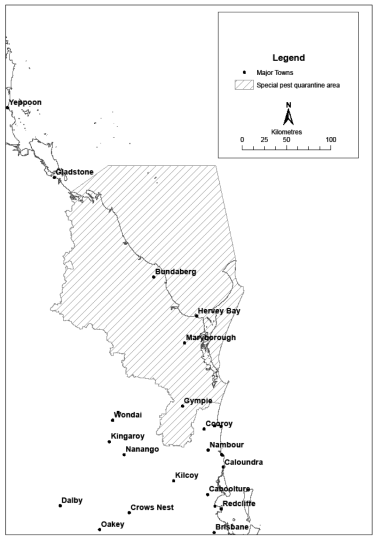
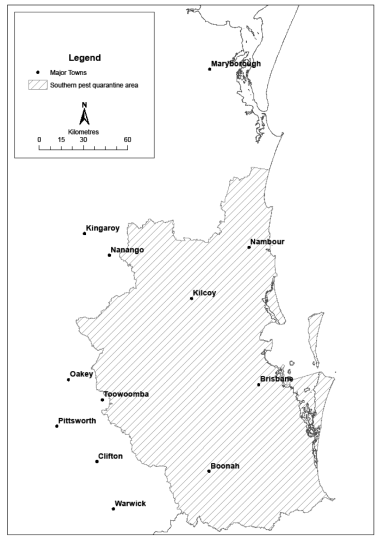
18Declaration of pest quarantine areas for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle
(1)Each area shown on a map in schedule 3 is declared to be a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle.(2)The exact location of the boundary of each of the pest quarantine areas is held in digital electronic form by the department.(3)Maps showing the exact location of the boundary of each of the pest quarantine areas can be accessed, free of charge, on the department’s website.(4)The information held in digital electronic form can be reduced or enlarged to show the details of the boundaries.s 18 sub 2008 SL No. 38 s 26
amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 5; 2013 SL No. 193 s 5
The objects of the quarantine for each pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, are—(a)to prevent the introduction into Queensland of pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle; and(b)to prevent the spread of pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle in Queensland; and(c)to prevent, control or remove infestations of pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle in the pest quarantine area.s 19 amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 6; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
sdiv 2 (ss 19A–19B) ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 7
19ADeclaration of pest quarantine area for tropical race 4
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for tropical race 4.sdiv 2 (ss 19A–19B) ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 7
The object of the quarantine for the pest quarantine area for tropical race 4 is to prevent the introduction into Queensland of tropical race 4.sdiv 2 (ss 19A–19B) ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 7
sdiv 3 (ss 19C–19D) ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 7
19CDeclaration of pest quarantine area for banana freckle
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for banana freckle.sdiv 3 (ss 19C–19D) ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 7
The object of the quarantine for the pest quarantine area for banana freckle is to prevent the introduction into Queensland of banana freckle.sdiv 3 (ss 19C–19D) ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 7
sdiv hdg ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 8
In this division—banana plant does not include the fruit of the plant.
sdiv hdg ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 9
21Restriction on introducing banana plants
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce a banana plant into Queensland unless the plant—(a)is a banana plantlet; and(b)is in a sealed pest-proof container; and(c)is accompanied by an inspector’s certificate, or assurance certificate, stating the plant is free from banana bunchy top, banana streak, cucumber mosaic, tropical race 4 and banana freckle; and(d)is transported in a way that prevents infestation by a banana plant pest.(2)In this section—banana plantlet means a banana plant that has been grown in a tissue culture medium in a closed container.banana plant pest see section 25.s 21 amd 2007 SL No. 258 s 3; 2013 SL No. 32 s 8; 2013 SL No. 193 s 10
Subdivision 3 Pest control measures for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle
sdiv hdg ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 11
22Restriction on moving banana plants into, out of or within a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a banana plant—(a)into a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle; or(b)from a parcel of land in a pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, to another parcel of land in the area; or(c)out of a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle.s 22 amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 9; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
23Restriction on moving soil, appliances and other things into, out of or within a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move soil on which a banana plant has been growing or an appliance or other thing that has been in contact with an infested plant or soil on which an infested plant has been growing—(a)into a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle; or(b)from a parcel of land in a pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, to another parcel of land in the area; or(c)out of a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle.(2)In this section—infested plant means a banana plant infested with 1 or more of the following—(a)bacterial wilt of banana, also known as—(i)banana blood disease; or(ii)banana bugtok disease; or(iii)banana moko disease;(b)fusarium wilt of banana, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Fusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f. sp. cubense (E.F. Smith) W.C. Snyder and H.N. Hansen, race 1, race 2 or subtropical race 4;(c)leaf spot of banana, also known as banana black Sigatoka disease.s 23 amd 2011 SL No. 202 s 4; 2013 SL No. 32 s 10; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
24Restriction on planting and cultivating banana plants in a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval—(a)plant a banana plant in a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle; or(b)cultivate a banana plant in a pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle.(2)However, a person may plant or cultivate a banana cultivar mentioned in schedule 4, parts 1 or 2, if the cultivar is planted and cultivated in—(a)a pest quarantine area for the part of the schedule in which the cultivar is in; and(b)a residential plantation.(3)An inspector may give an approval to plant or cultivate a pest banana plant only if satisfied the planting and cultivation are to be carried out—(a)for research or educational purposes; and(b)in a way that is not likely to spread the plant’s seed.(4)In this section—residential plantation means a group of no more than 10 banana plants or 30 pseudostems that are not cultivated for sale.s 24 amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 12; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
sdiv hdg ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 13
24ARestriction on moving soil, appliances and other things into the pest quarantine area for tropical race 4
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move any of the following things into the pest quarantine area for tropical race 4 if the thing has been despatched from another State in which tropical race 4 has been detected—(a)soil on which a banana plant has been growing;(b)an appliance or other thing that has been in contact with a banana plant or soil on which a banana plant has been growing.s 24A (prev s 23A) ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 11
amd 2013 SL No. 66 s 3
renum and reloc 2013 SL No. 193 s 12
sdiv 5 (s 24B) ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 14
24BRestriction on moving soil, appliances and other things into the pest quarantine area for banana freckle
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move any of the following things into the pest quarantine area for banana freckle if the thing has been despatched from another State in which banana freckle has been detected—(a)soil on which a banana plant has been growing;(b)the fruit of a banana plant;(c)an appliance or other thing that has been in contact with a thing mentioned in paragraph (a) or (b).sdiv 5 (s 24B) ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 14
In this division—banana plant pest means the following pests—(a)bacterial wilt of banana, also known as—(i)banana blood disease; or(ii)banana bugtok disease; or(iii)banana moko disease;(b)banana black Sigatoka disease.pest site means an area within approximately 50km of a place where a banana plant pest has been found.
(1)If the chief executive considers it necessary to prevent a banana plant pest spreading in Queensland, the chief executive may—(a)declare an area in a pest quarantine area to be a pest area; and(b)define the boundaries of the area so declared.(2)The chief executive must give notice of the declaration—(a)in a newspaper, if any, published at least 5 days in any week, and circulating generally throughout the locality in which the pest area is situated; or(b)in another newspaper published in Brisbane and circulating generally throughout Queensland.A copy of the notice may be inspected on the department’s website.(3)The notice must state the following—(a)that an area has been declared to be a pest area;(b)the location and boundaries of the area;(c)where a map showing the boundaries of the area is available for public inspection;(d)the restrictions on movement of fruit of a banana plant growing in the pest area.
(1)This section applies to fruit of a banana plant growing in a pest site if—(a)the chief executive declares the pest site to be a pest area under section 26; and(b)the person moves the fruit—(i)out of the pest area; or(ii)from a parcel of land in the pest area to another parcel of land in the area.(2)The person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move the fruit unless the person moves the fruit in a way that complies with the restrictions on movement of fruit stated in the declaration.
28Treatment methods A, B, C and D
Treatment methods A, B, C and D for treating banana plants under this part are described in schedule 5, items 1 to 4.s 28 amd 2013 SL No. 80 s 4
(1)The chief executive may approve a method (an approved treatment method) for treating banana plants as a method of discharging an obligation under any of sections 29 to 36.(2)The chief executive may approve a method under subsection (1) only if the chief executive is satisfied on reasonable grounds that the method is effective and appropriate, having regard to—(a)the purpose of the method; and(b)the associated risks to human health, the environment, trade, and crop and animal safety.(3)The chief executive must publish each approved treatment method on the department’s website.(4)An approval under subsection (1) expires 6 months after it is given or, if an earlier time is stated in the approval, at the earlier time.s 28A ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 5
(1)This section applies to an owner of land in a pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, if a banana plant is growing on the land in a pest site.(2)Unless the owner has an inspector’s approval stating the plant does not have to be treated under this section, the owner must—(a)treat the plant using treatment method B or C or an approved treatment method for this paragraph; and(b)fence off the pest site from other banana plants.(3)The owner must—(a)treat the plant and fence off the pest site within 1 day after becoming aware the pest has been found; and(b)as soon as practicable after the day the plant is treated, plant and grow ground cover vegetation on the pest site.(4)The owner must not, without an inspector’s approval, plant a banana plant on the pest site.(5)The owner must grow the ground cover vegetation on the pest site unless the owner has an inspector’s approval stating the vegetation need not be grown on the site.(6)In this section—pest site means an area within 20m of a place where bacterial wilt of banana, also known as the following, has been found—(a)banana blood disease;(b)banana bugtok disease;(c)banana moko disease.s 29 amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 13; 2013 SL No. 80 s 6; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
30Banana black Sigatoka disease
(1)This section applies to an owner of land in a pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, who grows a banana plant on the land within 500m of a place where banana black Sigatoka disease has been found.(2)Unless the owner has an inspector’s approval stating the plant does not have to be treated under this section, the owner must—(a)treat the plant’s leaf tissue that is dead or not green in colour by—(i)burning it or burying it under at least 60cm of soil; or(ii)using an approved treatment method for this paragraph; and(b)treat the plant using treatment method B, C or D or an approved treatment method for this paragraph.(3)The owner must—(a)treat the leaf tissue mentioned in subsection (2) (a) within 1 day after an inspector gives the owner a direction to treat the leaf tissue; and(b)treat the plant within 3 days after an inspector gives the owner a direction to treat the plant.(4)In this section—banana plant does not include a banana black Sigatoka resistant cultivar mentioned in schedule 6.s 30 amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 14; 2013 SL No. 80 s 7; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
(1)This section applies to an owner of land in a pest quarantine area if—(a)the owner grows a banana plant on the land; and(b)the plant is infested with banana bunchy top virus.(2)Unless the owner has an inspector’s approval stating the plant does not have to be treated under this section, the owner must—(a)spray the plant with dieseline or kerosene; and(b)treat it using treatment method A, B or C or an approved treatment method for this paragraph.(3)The owner must spray and treat the plant within 1 day after becoming aware the virus has been found.s 31 amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 15; 2013 SL No. 80 s 8
s 32 amd 2011 SL No. 202 s 5; 2013 SL No. 32 s 16; 2013 SL No. 80 s 9; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
om 2015 SL No. 185 s 3
(1)This section applies to an owner of land in a pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, if a pest banana plant is growing on the land.(2)Unless the owner has an inspector’s approval to grow the plant, the owner must, within 1 day after becoming aware the plant is on the land—(a)collect and burn the fruit and seeds of the plant; and(b)inject the plant’s pseudostem at a height of 30cm above the ground using—(i)either—(A)15ml of a 1% solution of 2,4-D; or(B)15ml of a 3.6% solution of glyphosate; or(ii)an approved treatment method for this paragraph.s 33 amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 17; 2013 No. 80 s 10; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
34Banana yellow Sigatoka and leaf speckle
(1)This section applies to an owner of land in a pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, if—(a)the owner grows a banana plant on the land; and(b)there is an infested leaf on the plant.(2)Unless the owner has an inspector’s approval stating the plant does not have to be treated under this section, the owner must treat each infested leaf by—(a)removing it from the plant and leaving it to rot on the surface of the soil; or(b)using an approved treatment method for this subsection.(3)The owner must treat each infested leaf within 7 days after the owner becomes aware it is an infested leaf.(4)In this section—infested leaf means a banana plant leaf that is infested with the banana yellow Sigatoka pest or banana leaf speckle pest and the visible symptoms of the infestation of either or both of the pests are showing—(a)if the banana plant is grown on land in the northern pest quarantine area—on more than 5% of the leaf; orSee schedule 3 (Pest quarantine areas for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle), part 3 (Northern pest quarantine area).(b)if the banana plant is grown on land in any other pest quarantine area for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle—(i)at any time between 1 November and 31 May—on more than 15% of the leaf; or(ii)at any time between 1 June and 31 October—on more than 30% of the leaf.s 34 amd 2002 SL No. 235 s 3; 2013 SL No. 32 s 18; 2013 SL No. 80 s 11; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
(1)This section applies to an owner of land in a pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, if a volunteer plant that is a banana plant is growing on the land.(2)The owner must, within 5 days after becoming aware the plant is on the land, treat it using treatment method A, B or C or an approved treatment method for this subsection.s 35 amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 19; 2013 SL No. 80 s 12; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
(1)If a person treats a banana plant under section 29 or 33, the person must treat any regrowth of the plant by spraying it with a 0.2% solution of 2,4-D or by using an approved treatment method for this subsection.(2)If a person treats a banana plant under section 30, 31 or 35, the person must treat any regrowth of the plant by—(a)either—(i)removing the regrowth from the soil and cutting it into pieces no more than 5cm in diameter; or(ii)spraying it with a 0.2% solution of 2,4-D; or(b)using an approved treatment method for this subsection.(3)The person must treat the regrowth as soon as practicable after becoming aware of it.s 36 amd 2013 SL No. 80 s 13; 2015 SL No. 185 s 4
37Keeping land free of weeds and other plants
An owner of land in a pest quarantine area, for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle, who grows a banana plant on the land must keep the land within 1m of the plant free from weeds or other plants that are—(a)more than 30cm high; and(b)growing in numbers that an inspector reasonably believes would be likely to hinder—(i)symptom expression of a pest infestation on the banana plant; or(ii)inspection of the banana plant by an inspector.s 37 amd 2009 SL No. 149 s 4; 2013 SL No. 32 s 20; 2013 SL No. 80 s 14; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
pt hdg (prev pt 6 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
In this part—approved risk management plan see section 55 (2).DPI fire ant approved symbol ...def DPI fire ant approved symbol ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 4 (2)
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 4
fire ant means the following pests—(a)tropical fire ant;(b)red imported fire ant.high risk item ...def high risk item sub 2003 SL No. 366 s 4 (1)–(2)
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 4
high risk restricted area means an area declared to be a high risk restricted area under section 49 (1) (a) (i).low risk restricted area means an area declared to be a low risk restricted area under section 49 (1) (a) (ii).pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 39.proposed risk management plan see section 56 (2) (a).restricted area means—(a)a high risk restricted area; or(b)a low risk restricted area.restricted item see section 38A.def restricted item sub 2003 SL No. 366 s 4 (1)–(2)
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 4
show cause period see section 60 (1) (e).soil includes a soil substitute that could be used as a growing medium for a plant.potting mix, organic mulchdef soil ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 4 (2)
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 4
treat—(a)for a restricted item to which an approved risk management plan relates—means treat in a way directed by the approved risk management plan; and(b)otherwise—means treat in a way directed by an inspector.def treat ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 4 (2)
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 4
s 38 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 4
(1)A restricted item means any of the following—(a)soil or any thing that has soil attached;turf, a plant that has soil on the plant’s roots, an appliance that has soil attached to it(b)material that is a product or by-product of quarrying or mining;chitters, coal fines, coal stone, decomposed granite, gravel, overburden(c)material that is a product or by-product of the processing or manufacturing of any of the following—(i)an animal;solid waste produced by processing an animal at an abattoir(ii)a plant;mulch, sawdust(iii)anything that comes from an animal or plant;animal manure, green waste(d)baled hay or straw.(2)Also, if an inspector decides any thing associated with a person’s commercial activity may spread fire ant, and notifies the person of the decision, the thing is a restricted item.s 38A ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 5
amd 2012 SL No. 224 s 5
39Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for fire ant.
The objects of the quarantine are—(a)to prevent fire ant spreading in Queensland; and(b)to eradicate it in Queensland; and(c)to prevent the introduction of tropical fire ant into Queensland.
41Restriction on moving live fire ants
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a live fire ant—(a)from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area; or(b)out of the pest quarantine area.
42Restriction on land owner’s movement of restricted items and other things
(1)This section applies to an owner of land if an inspector—(a)reasonably believes the land is infested with fire ant; and(b)gives the owner a written notice stating—(i)the land is infested with fire ant; and(ii)the things on the land the inspector reasonably believes are infested with fire ant.(2)The owner must not, without an inspector’s approval, move, or allow another person to move, a restricted item or other thing mentioned in subsection (1) (b) (ii)—(a)from the owner’s land to another parcel of land in the pest quarantine area; or(b)out of the pest quarantine area.
43Restriction on other person’s movement of restricted items and other things
(1)This section applies to a person carrying on a commercial activity in the pest quarantine area if an inspector—(a)reasonably believes the activity may spread fire ant in the pest quarantine area; and(b)gives the person a written notice stating—(i)that the activity may spread fire ant in the pest quarantine area; and(ii)the things associated with the activity the inspector reasonably believes may spread fire ant.(2)The person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move, or allow another person to move, a restricted item or other thing mentioned in subsection (1) (b) (ii)—(a)from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area; or(b)out of the pest quarantine area.(3)In deciding whether the activity or other thing may spread fire ant, the inspector must have regard to—(a)the nature of the activity or thing; and(b)where the activity is carried out.
In this subdivision—land does not include a dwelling house on the land.s 44 def land sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 8
45Obligation of land owner to allow surveillance
(1)If an inspector requires an owner of land in the pest quarantine area to allow the inspector to carry out surveillance on the land to look for and monitor the spread of fire ant, the owner must not refuse to allow the inspector to carry out surveillance.(2)Without limiting subsection (1), an inspector may carry out surveillance on the land by putting fire ant baits, lures or traps on the land.(3)The inspector may direct the owner to remove any thing on the land that would obstruct the inspector carrying out surveillance on the land.Examples of things an inspector may direct to be removed—
•rubbish•scrap metal•vegetation(4)When making the requirement or direction, the inspector must give the person an offence warning.s 45 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 6; 2011 SL No. 202 s 6
46Preventative treatment of land, plants and other things
(1)If an inspector considers it necessary to prevent fire ant spreading in the pest quarantine area, the inspector may require an owner of land in the pest quarantine area to allow the inspector to treat—(a)the land; or(b)a plant, or other thing the inspector reasonably believes may spread fire ant, on the land.(2)The owner must not refuse to allow the inspector to carry out the treatment.(3)The inspector may direct the owner to remove any thing on the land that would obstruct the inspector treating the land, or plant or other thing on the land.Examples of things an inspector may direct to be removed—
•rubbish•scrap metal•vegetation(4)When making the requirement or direction, the inspector must give the person an offence warning.s 46 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 7
47Obligation of owner of land in the vicinity of infested land
An owner of land in the vicinity of land infested with fire ant must, if directed by an inspector, monitor the owner’s land for fire ant in the way the inspector considers appropriate for finding fire ant.
s 47A ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 8
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 6
48Treatment of infested land, plants and other things
(1)If an inspector requires an owner of land infested with fire ant to allow an inspector or an authorised person to treat—(a)the land; or(b)a plant, or other thing infested with fire ant, on the land;the owner must not refuse to allow an inspector or authorised person to carry out the treatment.(2)When making the requirement, the inspector must give the person an offence warning.(3)In this section—authorised person means a person authorised by the chief executive.s 48 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 9
sdiv hdg sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
49Declaration of restricted area
(1)If the chief executive considers it necessary to prevent fire ant spreading or to eradicate fire ant in Queensland, the chief executive may—(a)declare an area in the pest quarantine area to be—(i)a high risk restricted area; or(ii)a low risk restricted area; and(b)define the boundaries of the area so declared.(2)The chief executive must give notice of the declaration in each of the following (each a declaration notice)—(a)in a newspaper published in Brisbane and circulating generally throughout Queensland;(b)in another newspaper, if any, published at least 5 days in any week, and circulating generally throughout the locality in which the area is situated;(c)on the department’s website.(3)A declaration notice must state each of the following—(a)a sufficient reference to the location of the area to identify the area;(b)that the area has been declared to be—(i)a high risk restricted area; or(ii)a low risk restricted area;(c)where a map showing the boundaries of the area is available for public inspection;(d)that the restrictions mentioned in sections 51 to 58 apply to the area.(4)A declaration notice under subsection (2) (a) or (b) must also state that the declaration notice on the website shows the boundaries of the area.(5)A declaration notice under subsection (2) (c) must also show the boundaries of the area.s 49 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 10
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
s 49A ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 12
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
sdiv hdg amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 11
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
This subdivision does not limit another provision of this part.s 50 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 13
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
51Restriction on moving infested thing
(1)An owner of land in a restricted area must not, without an inspector’s approval, move, or allow another person to move, a thing infested with fire ant—(a)from the owner’s parcel of land to another parcel of land in the restricted area; or(b)out of the restricted area.(2)The inspector may approve a movement mentioned in subsection (1) on conditions.s 51 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 14
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
s 51A ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 15
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
s 51B ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 15
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
s 51C ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 15
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
52Restriction on land owner’s movement of restricted item from land in high risk restricted area
(1)This section applies if the owner of a parcel of land in a high risk restricted area—(a)has a restricted item on the land; and(b)is not carrying on a commercial activity on the land.(2)The owner must not, without an inspector’s approval, move, or allow another person to move, the restricted item from the land.(3)The inspector may approve a movement mentioned in subsection (2) on conditions.(4)Despite subsection (2), the owner may move, or allow another person to move, the restricted item to a waste facility in the restricted area without an inspector’s approval.(5)In this section—waste facility see the Waste Reduction and Recycling Act 2011 , schedule.s 52 sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
53Restriction on moving restricted item by person carrying on commercial activity in high risk restricted area
(1)This section applies to a person carrying on a commercial activity in a high risk restricted area if the person has a restricted item on the site where the commercial activity is carried on.(2)The person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move, or allow another person to move, the restricted item—(a)from a parcel of land in the high risk restricted area to another parcel of land in the high risk restricted area; or(b)out of the high risk restricted area.(3)The inspector may approve a movement mentioned in subsection (2) on conditions.(4)Despite subsection (2), if there is an approved risk management plan for the activity, the person may carry out, or allow another person to carry out, a movement mentioned in subsection (2) without an inspector’s approval if the restricted item has been treated in compliance with the plan.For the requirement to have a risk management plan for a commercial activity in a restricted area that involves the movement of a restricted item, see section 55.s 53 sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
s 53A ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 16
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
54Restriction on moving restricted item by person carrying on commercial activity in low risk restricted area
(1)This section applies to a person carrying on a commercial activity in a low risk restricted area if the person has a restricted item on the site where the commercial activity is carried on.(2)The person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move, or allow another person to move, the restricted item out of the low risk restricted area.(3)The inspector may approve the movement on conditions.(4)However, the person may carry out, or allow another person to carry out, the movement without an inspector’s approval if—(a)the person moves the restricted item to a high risk restricted area; or(b)if there is an approved risk management plan for the commercial activity—the restricted item has been treated in compliance with the plan.For the requirement to have a risk management plan for a commercial activity in a restricted area that involves the movement of a restricted item, see section 55.s 54 sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
sdiv hdg sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
55Person carrying on certain commercial activity in restricted area must have approved risk management plan
(1)This section applies to a person who is carrying on a commercial activity—(a)in a high risk restricted area, if the commercial activity involves the movement of a restricted item—(i)from a parcel of land in the high risk restricted area to another parcel of land in the high risk restricted area; or(ii)out of the high risk restricted area; or(b)in a low risk restricted area, if the commercial activity involves the movement of a restricted item out of the low risk restricted area, other than to land in a high risk restricted area.(2)The person must implement and keep a risk management plan that complies with section 56 for the commercial activity (an approved risk management plan).(3)However, this section does not apply to a person if—(a)for the movement of a restricted item mentioned in subsection (1) (a)—the person obtains an inspector’s approval under section 53 before carrying out the movement; or(b)for the movement of a restricted item mentioned in subsection (1) (b)—the person obtains an inspector’s approval under section 54 before carrying out the movement.s 55 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 17
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
amd 2015 SL No. 185 s 5
56Requirements for risk management plan
(1)A risk management plan must manage the risks associated with the commercial activity carried on in a restricted area by a person by using appropriate management techniques to prevent the activity, or the things associated with the activity, from spreading fire ant.(2)The person carrying on the commercial activity must—(a)prepare a risk management plan for the commercial activity (the proposed risk management plan); and(b)give the proposed risk management plan to an inspector.(3)The proposed risk management plan has no effect unless it has been approved by an inspector.s 56 amd 2003 SL No. 366 s 18
sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
57Approval of proposed risk management plan
(1)An inspector must, when deciding whether to approve a proposed risk management plan, consider if it—(a)takes into account the risks posed by the commercial activity that may spread fire ant; and(b)identifies each restricted item or procedure that may spread fire ant; and(c)ensures each restricted item is not infested with fire ant.(2)The factors the inspector must consider, if applicable to the commercial activity, include, but are not limited to, the following—(a)purchase of restricted items;(b)movement of restricted items onto and off the site where the commercial activity is carried on;(c)storage and use of restricted items on the site;(d)methods to increase the early detection of fire ant on the site;(e)monitoring of the site to detect the presence of fire ant;(f)treatment for fire ant at the site;(g)treatment of a restricted item before moving the item off the site;(h)staff training on detection of fire ant.(3)The person carrying on the commercial activity must give information the inspector reasonably requires to decide whether the plan should be approved.(4)Before approving the proposed risk management plan, the inspector may—(a)inspect, test or treat or take samples of a restricted item; or(b)do anything else the inspector reasonably considers necessary or desirable.(5)The inspector may approve a person’s proposed risk management plan subject to conditions.s 57 sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
58Term of approved risk management plan
An approved risk management plan remains in force—(a)for any term stated initially in it; or(b)for any term an inspector later directs; or(c)until it is cancelled or suspended.s 58 sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
An inspector may audit an approved risk management plan to decide if it has been satisfactorily implemented and kept under this part.s 58A ins 2012 SL No. 224 s 7
59Grounds for cancellation and suspension
Each of the following is a ground for cancelling or suspending a person’s approved risk management plan—(a)an inspector reasonably believes the person has not complied with the plan;(b)the approval was obtained by incorrect or misleading information or documents;(c)the person has not complied with—(i)a condition of the approval; or(ii)a direction by an inspector to amend the plan.s 59 amd 2012 SL No. 224 s 8
60Procedure for cancellation and suspension—general
(1)If an inspector considers a ground exists to cancel or suspend a person’s approved risk management plan, the inspector must give the person written notice stating each of the following—(a)the proposed action;(b)the grounds for the proposed action;(c)the facts and circumstances that form the basis for the grounds;(d)if the proposed action is a suspension—the proposed suspension period;(e)that the person may make, within a stated period (the show cause period), written representations to show why the proposed action should not be taken.(2)The show cause period must end at least 14 business days after the person is given the notice.(3)If the inspector decides to take the proposed action, the inspector must, within 5 business days after making the decision, inform the person of the decision by written notice.(4)The decision takes effect when the notice is given.s 60 amd 2012 SL No. 224 s 9
(1)This section applies despite sections 59 and 60.(2)If an inspector considers it necessary to prevent fire ant spreading or to eradicate fire ant in Queensland, the inspector may, by written notice to a person, immediately suspend the person’s approved risk management plan until the earlier of the following—(a)the inspector informs the person of the inspector’s decision by notice under section 60 (3), given after complying with section 60 (1) and (2);(b)the end of 60 days after notice to the person.s 61 amd 2012 SL No. 224 s 10
62Notice of decision and reconsideration
If the inspector cancels, suspends or immediately suspends an approval, the notice under section 60 (3) or 61 (2) must state—(a)the decision, and the reasons for it; and(b)that the person may apply to the chief executive under section 21M of the Act for reconsideration of the decision; and(c)how to apply.s 62 amd 2009 Act No. 24 s 682
63Live tropical fire ants and infested things
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce the following into Queensland—(a)a live tropical fire ant;(b)any thing the person reasonably believes may be infested with tropical fire ant.(2)An inspector may give an approval only if the inspector is satisfied the introduction of the thing will not pose a significant risk of introducing tropical fire ant into Queensland.
(1)This section applies for restricted items that come from another State in which tropical fire ant is known to be living.(2)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce the restricted item into Queensland.(3)An inspector may give an approval only if the restricted item is accompanied by a certificate, from an interstate inspector, that states—(a)the item is dispatched from a property that is more than 5km from an infestation of tropical fire ant; or(b)the item, when inspected by the interstate inspector, was free from evidence of tropical fire ant.
div hdg ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv hdg ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
s 64A ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
s 64B ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
def scheme period amd 2008 SL No. 116 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv 2 (ss 64C–64J) ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv 2 (ss 64C–64J) ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv 2 (ss 64C–64J) ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv 2 (ss 64C–64J) ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv 2 (ss 64C–64J) ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv 2 (ss 64C–64J) ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv 2 (ss 64C–64J) ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
sdiv 2 (ss 64C–64J) ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 3
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 11
pt hdg (prev pt 7 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
In this part—authorised person means a person authorised by—(a)the chief executive of an interstate department; or(b)an interstate inspector.fire blight area means an area in a State, other than Queensland, where there is an infestation of fire blight.pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 66.regulated fire blight host plant, for a fire blight area, means a plant that—(a)is—(i)a hybrid mentioned in schedule 7; or(ii)of a species mentioned in schedule 7; or(iii)of a species within a genus mentioned in schedule 7; and(b)has—(i)for fruit—been grown within 5km of the fire blight area; or(ii)for a plant (other than fruit)—been within 20km of the fire blight area.s 65 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
66Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for fire blight.
The object of the quarantine is to prevent the introduction of fire blight into Queensland.
68Restriction on introducing regulated fire blight host plant
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce a regulated fire blight host plant into Queensland.(2)However, the person may introduce the plant, other than its fruit, if—(a)the plant has been grown in a nursery that has been certified, by an interstate inspector, to be—(i)located more than 10km from a fire blight area; and(ii)free from evidence of fire blight when inspected by an interstate inspector in the autumn and spring before the certificate was made; and(b)the plant is accompanied by a certificate, from an interstate inspector or authorised person, that states the plant was growing in the nursery for the entire year before the certificate was made.
pt hdg (prev pt 8 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
div hdg ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 3
In this part—clarified juice means juice of grapes—(a)that is visibly clear; and(b)from which solids have been removed such that it contains no more than 1% of solids.filtered juice means clarified juice processed through a filter that removes all particles larger than 50 microns in diameter.fresh juice means the liquid fraction from must that—(a)excludes skins, seeds and other large solids; but(b)may contain some suspended solids.fruit of a grape plant includes whole table grapes and whole wine grapes.general control zone ...def general control zone ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 4 (2)
om 2013 SL No. 80 s 2 sch
grape phylloxera means the pest Daktulosphaira vitifolii (Fitch).def grape phylloxera ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 4 (2)
grape plant means a grape plant Vitis spp. and includes the following—(a)vine cuttings, buds and vegetative tissue (or plant parts) for propagation;(b)germplasm establishment cuttings;(c)any vegetative part of the grape plant.def grape plant amd 2013 SL No. 80 s 15 (3)
grape plant product, of a grape plant, means a product derived from the plant and includes—(a)fruit of the grape plant; and(b)clarified juice, filtered juice, fresh juice, marc and must.def grape plant product amd 2010 SL No. 119 s 4 (3)
marc, for grapes, means—(a)the solids residue from crushing or pressing of must; or(b)wine fermented on skins, containing skins, seeds and possibly stems.def marc sub 2010 SL No. 119 s 4 (1)–(2)
must, for grapes, means the total product of crushing grape berries and includes juice, skins, seeds, pulp, and possibly some stems and leaves.other thing includes—(a)machinery, tools and vehicles; and(b)any other equipment used in a vineyard, including grape bins and packaging material.def other thing ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 4 (2)
sub 2013 SL No. 80 s 15 (1)–(2)
pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 70.phylloxera exclusion zone see section 73 (1).def phylloxera exclusion zone ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 2 sch
phylloxera risk zone means the part of the pest quarantine area that is outside the phylloxera exclusion zone.def phylloxera risk zone ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 2 sch
special control zone ...def special control zone ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 4 (2)
om 2013 SL No. 80 s 2 sch
vineyard soil means soil that has been within 100m of a living grapevine.def vineyard soil ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 15 (2)
s 69 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
div hdg ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 5
70Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for grape phylloxera.
The objects of the quarantine are to—(a)prevent the introduction of grape phylloxera into Queensland; and(b)prevent or control the spread of grape phylloxera within Queensland; and(c)remove infestations of grape phylloxera in Queensland.s 71 sub 2010 SL No. 119 s 6
div hdg ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 6
amd 2013 SL No. 80 s 2 sch
72Restriction on introducing restricted items
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce any of the following (each a restricted item) into the phylloxera risk zone from outside the quarantine area—(a)grape phylloxera;(b)a grape plant;(c)a grape plant product;(d)an appliance or other thing that has been in contact with a grape plant or the soil on which a grape plant has been growing;(e)vineyard soil.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, only if the inspector is satisfied that the introduction of the restricted item will not pose a significant risk of introducing grape phylloxera into the phylloxera risk zone.s 72 sub 2010 SL No. 119 s 6
amd 2013 SL No. 80 ss 16, 2 sch
div hdg ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 6
amd 2013 SL No. 80 s 2 sch
73What is the phylloxera exclusion zone
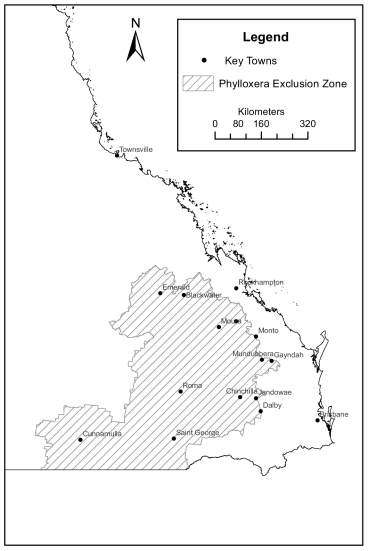
(1)The phylloxera exclusion zone is the area made up of—(a)the following local government areas—(i)Balonne shire;(ii)Banana shire;(iii)Central Highlands region;(iv)Maranoa region;(v)Paroo shire;(vi)Woorabinda Aboriginal shire; and(b)the part of the local government area of North Burnett region west of the Burnett Highway; and(c)the part of the local government area of Western Downs region west of a line—•from the intersection of the boundary of the Western Downs region with the Dalby Cecil Plains Road north to the intersection with the Warrego Highway•along the Warrego Highway to the intersection with Dalby Jandowae Road•along Dalby Jandowae Road in a northerly direction to the intersection with Kingaroy Jandowae Road•along Kingaroy Jandowae Road in an easterly direction to the intersection with Niagra Road•along Niagra Road in an easterly direction to the intersection with the Bunya Highway•along the boundary of the Western Downs region in a northerly direction to the intersection with the boundary of the North Burnett region.(2)Attachment 1 to this regulation shows the approximate location of the phylloxera exclusion zone.Maps showing the exact location of the boundary of the phylloxera exclusion zone in particular places are available, free of charge, from the department’s head office in Brisbane and its regional offices in the phylloxera exclusion zone. The addresses and contact details for the department’s offices can be found on the department’s website.(3)The attachment does not form part of this regulation.(4)If the phylloxera exclusion zone is amended the attachment must be revised as soon as possible after the amendment.s 73 sub 2010 SL No. 119 s 6
amd 2013 SL No. 80 ss 17, 2 sch
74Restriction on introducing restricted items
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce into the phylloxera exclusion zone, any of the following (each a restricted item)—(a)grape phylloxera;(b)a grape plant;(c)a grape plant product;(d)an appliance or other thing that has been in contact with a grape plant or the soil on which a grape plant has been growing;(e)vineyard soil.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, only if the inspector is satisfied that the introduction of the restricted item will not pose a significant risk of introducing grape phylloxera into the phylloxera exclusion zone.(3)To remove any doubt, it is declared that a person requires an approval under subsection (2) to introduce a restricted item into the phylloxera exclusion zone even if the person has been given an approval under section 72 (2) to introduce the item into the phylloxera risk zone.s 74 sub 2010 SL No. 119 s 6
amd 2013 SL No. 80 ss 18, 2 sch
pt hdg (prev pt 9 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
In this part—authorised person means a person authorised (by the chief executive, or an interstate inspector, of an interstate department of the State in which mango leafhopper has been detected and a mango plant was grown or despatched) to—(a)competently treat the mango plant in an approved way; and(b)issue a treatment certificate.pest quarantine area means a pest quarantine area declared under section 76.def pest quarantine area sub 2005 SL No. 332 s 3
treatment certificate, for a plant, means a certificate stating the plant has been treated in an approved way.s 75 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
div hdg sub 2005 SL No. 332 s 4
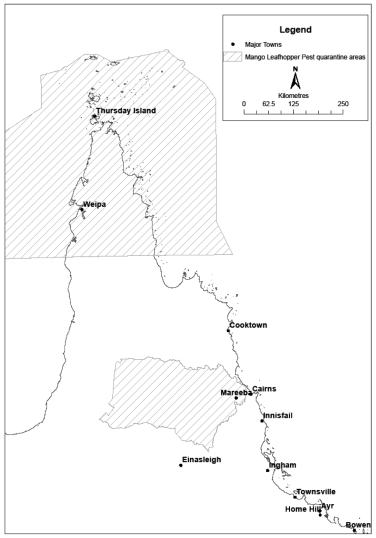
76Declaration of pest quarantine areas
(1)Each area shown on the map in schedule 7A is declared to be a pest quarantine area for mango leafhopper.(2)The exact location of the boundary of each of the pest quarantine areas is held in digital electronic form by the department.(3)A map showing the exact location of the boundary of each of the pest quarantine areas can be accessed, free of charge, on the department’s website.(4)The information held in digital electronic form can be reduced or enlarged to show the details of the boundaries.s 76 sub 2005 SL No. 332 s 4; 2008 SL No. 38 s 27
The objects of the quarantine are—(a)to prevent mango leafhopper being brought out of a pest quarantine area; and(b)to prevent the spread of mango leafhopper in a quarantine area; and(c)for the pest quarantine area declared under section 76 (1)—to prevent the introduction of mango leafhopper into Queensland.s 77 sub 2005 SL No. 332 s 4
amd 2009 SL No. 149 s 5
78Restriction on introducing mango leafhopper and infested plant
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce into Queensland—(a)mango leafhopper, or(b)a plant infested with mango leafhopper.
79Restriction on introducing mango plant
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce into Queensland a mango plant grown in or despatched from another State in which mango leafhopper has been detected.(2) Subsection (1) does not apply—(a)to the fruit of the mango plant if the stem of the fruit is removed at the abscission layer; or(b)to a mango plant if it is accompanied by a treatment certificate for the plant issued by—(i)an interstate inspector; or(ii)an authorised person.
80Restrictions on movement out of pest quarantine area
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a mango leafhopper, or a prescribed part of a mango plant, out of a pest quarantine area.(2)An inspector may give an approval under subsection (1) only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the mango leafhopper or prescribed part will not pose a significant risk of spreading mango leafhopper in Queensland.(3)In this section—prescribed part, of a mango plant, means a part of the mango plant other than the fruit of the plant and any stems attached to the fruit.s 80 sub 2005 SL No. 332 s 5
81Restrictions on movement within pest quarantine area
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a mango leafhopper, or a plant infested with mango leafhopper, from a parcel of land within a pest quarantine area to another parcel of land within the area.(2)An inspector may give an approval under subsection (1) only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the mango leafhopper or plant will not pose a significant risk of spreading mango leafhopper in the pest quarantine area.s 81 sub 2005 SL No. 332 s 5
pt hdg (prev pt 10 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
amd 2007 SL No. 19 s 3
In this part—pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 83.s 82 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
83Declaration of pest quarantine area
The area north of latitude 13º45' south is declared to be a pest quarantine area for mango caterpillar.Latitude 13º45' south passes near Coen.
The object of the quarantine is to prevent mango caterpillar spreading in Queensland.
85Restriction on moving live mango caterpillars and mango plants
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a live mango caterpillar or a mango plant—(a)from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area; or(b)into or out of the pest quarantine area.
pt hdg (prev pt 11 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
In this part—approved condition, for a plant, means the plant is in a condition approved by the chief executive or an inspector.host plant means a plant mentioned in schedule 8.pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 87.s 86 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
87Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for Mediterranean fruit fly.
The object of the quarantine is to prevent the introduction of Mediterranean fruit fly into Queensland.
89Restriction on introducing Mediterranean fruit fly and infested plant
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce into Queensland—(a)Mediterranean fruit fly; or(b)a plant infested with Mediterranean fruit fly.(2)An inspector may give an approval only if the inspector is satisfied the introduction of Mediterranean fruit fly or the plant will not pose a significant risk of introducing Mediterranean fruit fly into Queensland.
90Restriction on introducing Mediterranean fruit fly host plant
(1)This section applies for a host plant, if the host plant has been grown at or comes from a place that is within 15km of an infestation of Mediterranean fruit fly.(2)A person must not introduce the host plant into Queensland unless—(a)for a host plant mentioned in schedule 8, part 1—an inspector approves the introduction of the plant; or(b)for a host plant mentioned in schedule 8, part 2—the plant has been harvested in a mature green condition; or(c)for a host plant mentioned in schedule 8, part 3—the plant’s skin has not been broken and the flesh has not been exposed when the plant was harvested.(3)An inspector may give an approval under subsection (2) (a) only if the inspector is satisfied the host is free from evidence of Mediterranean fruit fly and the plant—(a)has been treated for Mediterranean fruit fly; or(b)is in an approved condition.s 90 amd 2007 SL No. 19 s 4
pt hdg (prev pt 12 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
In this part—pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 92.s 91 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
92Declaration of pest quarantine area
The area south of latitude 24º30' south and east of longitude 150º00' east is declared to be a pest quarantine area for papaya ringspot.Latitude 24º30' south, longitude 150º00' east is in the vicinity of Moura.
The object of the quarantine is to prevent papaya ringspot being brought out of the pest quarantine area.
94Restriction on moving prohibited plants
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, bring a prohibited plant out of the pest quarantine area.(2)An inspector may give an approval under subsection (1) only if the inspector is satisfied the plant is free of papaya ringspot.(3)In this section—plant does not include the fruit or seed of the plant.prohibited plant means—(a)a plant of the genus Carica; or(b)a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae.Example for paragraph (a) of a plant of the genus Carica—
papaya plantExamples for paragraph (b) of plants of the family Cucurbitaceae—
•cucumber•melon•pumpkin•squash
pt hdg (prev pt 13 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
In this part—pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 96.potato pest means the following pests—(a)golden nematode;(b)potato cyst nematode.potato pest area means an area in a State, other than Queensland, within 20km of an infestation of a potato pest.restricted item means the following—(a)soil;(b)a plant of the Solanaceae family.Examples of plants of the Solanaceae family—
•capsicum•potato•thornapple•tobacco•tomatos 95 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
96Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for potato pest.
The object of the quarantine is to prevent the introduction into Queensland of potato pest.
98Introduction of restricted item
(1)A person must not introduce a restricted item into Queensland if the restricted item has been in a potato pest area unless—(a)an inspector has given approval; and(b)if the approval is given on conditions, the person has complied with the conditions.(2)An inspector may give an approval under subsection (1) only if the inspector is satisfied the introduction of the restricted item will not pose a significant risk of introducing potato pest into Queensland.s 98 sub 2004 SL No. 4 s 3
(1)A person must not introduce a thing, other than a restricted item, into Queensland if the thing has come from a potato pest area unless—(a)the thing is accompanied by a certificate from an interstate inspector that states potato pest does not exist at the place; or(b)an inspector has given approval and, if the approval is given on conditions, the person has complied with the conditions; or(c)the thing is not a plant and all soil has been removed from it.(2)An inspector may give an approval only if the inspector is satisfied the introduction of the thing will not pose a significant risk of introducing potato pest into Queensland.
100Restrictions on planting potato tuber
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, plant a potato tuber if the potato tuber—(a)has been in a potato pest area; and(b)is not substantially free of soil.
pt hdg (prev pt 14 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
om 2013 SL No. 80 s 19
s 101 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2013 SL No. 80 s 19
s 102 om 2013 SL No. 80 s 19
s 103 om 2013 SL No. 80 s 19
s 104 om 2013 SL No. 80 s 19
s 105 om 2013 SL No. 80 s 19
pt hdg (prev pt 15 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
pt 11 div 1 sdiv 2 hdg om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
pt 11 div 1 sdiv 3 hdg om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
div hdg sub 2007 SL No. 185 ss 3, 5
s 106 om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
def bureau chief executive om 2003 SL No. 211 s 4 (1)
def clearance certificate amd 2003 SL No. 211 s 4 (2)
om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
s 107 om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
s 108 sub 2006 SL No. 179 s 4
om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
s 109 om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
s 110 om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
s 111 om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
s 112 om 2007 SL No. 185 s 3
In this part—pest quarantine area means each of the pest quarantine areas declared under section 114.sugarcane plant ...def sugarcane plant ins 2007 SL No. 185 s 6 (3)
om 2008 SL No. 17 s 3
sugarcane plant pest means a pest mentioned in schedule 11.s 113 amd 2007 SL No. 185 s 6 (1)–(2)
div hdg sub 2007 SL No. 185 ss 4, 7
114Declaration of pest quarantine areas
(1)Each area described in schedule 10 is declared to be a pest quarantine area for a sugarcane plant pest.Maps of the quarantine areas are available for inspection at the department’s head office and at the following places—(a)Maroochy Research Station at Mayers Road, Nambour;(b)Centre for Wet Tropics Research at South Johnstone Road, South Johnstone;(c)the department’s regional office at 21 Redden Street, Cairns.(2)Attachment 2 to this regulation shows the approximate location of each pest quarantine area.(3)The attachment—(a)does not form part of this regulation; and(b)must be revised if the area of a pest quarantine area is amended.(4)The revision must be made when the pest quarantine area is amended.
The objects of the quarantine for each pest quarantine area are—(a)to prevent the introduction into Queensland of sugarcane plant pests; and(b)to prevent the spread of the pests in Queensland; and(c)to control or remove pest infestation of sugarcane plants in the pest quarantine area.
div hdg amd 2007 SL No. 185 s 8
116Restriction on introducing sugarcane plant
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce a sugarcane plant into Queensland.(2)An inspector may give an approval only if the inspector is satisfied the introduction of the plant will not pose a significant risk of introducing a sugarcane plant pest into Queensland.
117Restriction on moving sugarcane plant
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a sugarcane plant—(a)into a pest quarantine area; or(b)out of a pest quarantine area.s 117 amd 2007 SL No. 185 s 9
118Restriction on moving appliances
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move into or out of a pest quarantine area—(a)an appliance that has been in contact with a sugarcane plant; or(b)soil on which a sugarcane plant is growing or has been growing.
118ARestriction on planting and cultivating non-approved sugarcane variety
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, plant or cultivate in a pest quarantine area a variety of sugarcane that is not, under section 11A of the Act, declared by the chief executive to be an approved plant variety for planting or cultivating in the area.See the Plant Protection (Approved Sugarcane Varieties) Declaration 2003 .s 118A ins 2003 SL No. 211 s 5
119Restriction on planting infested plant
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, plant an infested plant in a pest quarantine area.(2)An inspector may give an approval only if the inspector is satisfied the planting is to be carried out—(a)for research or educational purposes; and(b)in a way that is not likely to spread the pest.(3)In this section—infested plant means a sugarcane plant infested with a sugarcane plant pest.
120Restriction on cultivating sugarcane plant infested with sugarcane Fiji disease
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, cultivate a sugarcane plant infested with sugarcane Fiji disease.(2)An inspector may give an approval only if the inspector is satisfied the cultivation is to be carried out—(a)on conditions in the approval; and(b)in a way that is not likely to spread sugarcane Fiji disease—(i)in a pest quarantine area; or(ii)out of a pest quarantine area.
121Restriction on cultivating sugarcane plant infested with sugarcane plant pest other than sugarcane smut
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, cultivate a sugarcane plant infested with a sugarcane plant pest, other than sugarcane smut, after the plant’s fourth year of cultivation.(2)In this section—fourth year of cultivation, for a sugarcane plant, means the fourth year after planting the plant.s 121 amd 2007 SL No. 185 s 10
122Restriction on moving sugarcane plant infested with sugarcane plant pest
(1)This section applies to an owner of land in a pest quarantine area if the owner is growing a sugarcane plant infested with a sugarcane plant pest on the land.(2)The owner must not, without an inspector’s approval, move, or allow another person to move, a plant—(a)from the owner’s land to another person’s parcel of land in the pest quarantine area; or(b)out of the pest quarantine area.(3)This section does not apply to a person who is moving sugarcane from the owner’s land directly to a mill in the pest quarantine area.s 122 amd 2007 SL No. 185 s 11
pt hdg prev pt 12 hdg (prev pt 16 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres pt 12 hdg ins 2008 SL No. 17 s 4
In this part—Asian sugarcane planthopper means the pest Perkinsiella thompsoni (Muir).Perkinsiella thompsoni is a species within the genus Perkinsiella, by reference to which the sugarcane planthopper is prescribed as a pest under schedule 1.pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 124.s 123 prev s 123 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres s 123 ins 2008 SL No. 17 s 4
124Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for Asian sugarcane planthopper.s 124 prev s 124 om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres s 124 ins 2008 SL No. 17 s 4
The objects of the quarantine are—(a)to prevent the movement of Asian sugarcane planthopper into the pest quarantine area; and(b)to prevent or control the spread of Asian sugarcane planthopper in areas in the pest quarantine area in which sugarcane is commercially produced; and(c)to control or remove pest infestation of Asian sugarcane planthopper in the pest quarantine area.s 125 prev s 125 om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres s 125 ins 2008 SL No. 17 s 4
126Restriction on moving Asian sugarcane planthopper
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move Asian sugarcane planthopper—(a)into the pest quarantine area; or(b)from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area.s 126 prev s 126 om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres s 126 ins 2008 SL No. 17 s 4
126ARestriction on moving appliances
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move an appliance that has been in contact with a sugarcane plant that comes from an area infested with Asian sugarcane planthopper—(a)into the pest quarantine area; or(b)from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the appliance will not pose a significant risk of—(a)introducing Asian sugarcane planthopper into the pest quarantine area; or(b)spreading Asian sugarcane planthopper in the pest quarantine area.s 126A ins 2008 SL No. 17 s 4
126BRestriction on moving sugarcane plants
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a sugarcane plant that comes from an area infested with Asian sugarcane planthopper—(a)into the pest quarantine area; or(b)from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the sugarcane plant will not pose a significant risk of—(a)introducing Asian sugarcane planthopper into the pest quarantine area; or(b)spreading Asian sugarcane planthopper in the pest quarantine area.s 126B ins 2008 SL No. 17 s 4
pt hdg (prev pt 17 hdg) renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
pt 13 div 6 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
pt 13 div 7 hdg ins 2005 SL No. 87 s 4
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
In this part—pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 128.targeted pest means a pest mentioned in schedule 12.s 127 amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
128Declaration of pest quarantine area
The area north of latitude 13º45' south is declared to be a pest quarantine area for a targeted pest.Latitude 13º45' south passes near Coen.
The objects of the quarantine are—(a)to prevent a targeted pest being brought out of the pest quarantine area; and(b)to prevent its spread in the pest quarantine area.s 129 amd 2004 SL No. 101 s 3; 2011 SL No. 202 s 7
130Restriction on moving targeted pest and plant infested with targeted pest out of pest quarantine area
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move the following out of the pest quarantine area—(a)a targeted pest;(b)a plant infested with a targeted pest.(2)An inspector may give an approval only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the targeted pest or plant will not pose a significant risk of spreading the targeted pest in Queensland.
131Restriction on moving plant infested with targeted pest within pest quarantine area
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a plant infested with a targeted pest within the pest quarantine area.(2)An inspector may give an approval only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the targeted pest or plant will not pose a significant risk of spreading the targeted pest in the pest quarantine area.
s 131V ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
s 131W ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
s 131X om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
s 131Y om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
s 131Z om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
s 131ZA om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
132Treatment of targeted pest or infested plant
(1)This section applies to a person moving a targeted pest or a plant infested with a targeted pest within or out of the pest quarantine area.(2)If an inspector directs the person to treat the targeted pest or infested plant, the person must carry out the treatment in the way directed by the inspector.(3)If an inspector directs the person to allow the inspector to treat the targeted pest or infested plant, the person must not refuse to allow the inspector to carry out the treatment.(4)When making the direction, the inspector must give the person an offence warning.prev s 132 (orig s 131A) ins 2004 SL No. 101 s 4
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres s 132 ins 2007 SL No. 19 s 6
pt hdg prev pt 14 hdg (prev pt 17A hdg) ins 2004 SL No. 101 s 4
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres pt 14 hdg ins 2008 SL No. 134 s 3
In this part—branched broomrape means the pest Orobanche ramosa L. (common name—branched broomrape).pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 134.prev s 133 (prev s 131B) ins 2004 SL No. 101 s 4
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres s 133 ins 2008 SL No. 134 s 3
134Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for branched broomrape.s 134 prev s 134 (prev s 131C) ins 2004 SL No. 101 s 4
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres s 134 ins 2008 SL No. 134 s 3
The objects of the quarantine are—(a)to prevent the introduction of branched broomrape into the pest quarantine area; and(b)to prevent or control the spread of branched broomrape in the pest quarantine area; and(c)to control or remove pest infestation of branched broomrape in the pest quarantine area.s 135 prev s 135 (prev s 131D) ins 2004 SL No. 101 s 4
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 5
pres s 135 ins 2008 SL No. 134 s 3
135ARestriction on moving branched broomrape
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move branched broomrape—(a)into the pest quarantine area; or(b)from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the branched broomrape will not pose a significant risk of spreading branched broomrape in the pest quarantine area.s 135A ins 2008 SL No. 134 s 3
135BRestriction on moving high risk items
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a high risk item that the person knows, or ought reasonably to know, has been in a branched broomrape pest area—(a)into the pest quarantine area; or(b)from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the high risk item will not pose a significant risk of—(a)introducing branched broomrape into the pest quarantine area; or(b)spreading branched broomrape in the pest quarantine area.(3)In this section—branched broomrape pest area means an area in a State, other than an area in Queensland, within 50km of an infestation of branched broomrape.high risk item means any of the following—(a)soil;(b)an appliance;(c)an animal kept, or usually kept, for a domestic purpose or in a captive state;(d)a plant.plant includes—(a)grain, legumes and oilseed; and(b)fodder made from a crop plant; and(c)fruit and vegetables; and(d)the part of a crop plant remaining after its seed is harvested.s 135B ins 2008 SL No. 134 s 3
pt hdg (orig pt 17B hdg) prev pt 15 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 10
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pres pt 15 hdg ins 2016 SL No. 46 s 3
pt 15 div 1 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pt 15 div 2 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pt 15 div 3 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pt 15 div 3 sdiv 1 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pt 15 div 3 sdiv 2 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pt 15 div 4 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pt 15 div 5 hdg ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
In this part—pyriform scale means the pest pyriform scale (Protopulvinaria pyriformis) (Cockerell).s 136 (orig s 131E) prev s 136 ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pres s 136 ins 2016 SL No. 46 s 3
def affected area om 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (1)
def affected area sign om 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (1)
def Agvet Code om 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (1)
def approved disinfectant om 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (1)
def authorised person sub 2004 SL No. 232 s 3
def canker amd 2005 SL No. 87 s 3 (2)
def canker bacterium ins 2005 SL No. 87 s 3 (1)
def canker direction om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def consumption movement ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (2)
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def destroy ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (2)
def export movement ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (2)
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def interstate produce number om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def native citrus plant ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (2)
def nominated herbicide ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (2)
def non-citrus plant ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (2)
def non-quarantined area om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def pest quarantine area amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
def prescribed conditions om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def prescribed matters om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def prescribed way, for inspecting host plants in a consignment om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def prescribed way, for inspecting kaffir lime leaves to be used for culinary purposes amd 2006 SL No. 171 s 3
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def prescribed way, for inspecting the fruit of host plants in a consignment om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def prescribed way, for writing prescribed matters on a package om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def relevant host plant ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 3 (2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
def treatment method A om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def treatment method A product om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def treatment method B om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def treatment method C om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def treatment method D om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def treatment method D product om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
def treatment method E om 2007 SL No. 19 s 7
137Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for pyriform scale.s 137 (orig s 131F) prev s 137 ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pres s 137 ins 2016 SL No. 46 s 3
The object of the quarantine is to prevent the introduction of pyriform scale into Queensland.s 138 (orig s 131G) prev s 138 ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
amd 2007 SL No. 19 s 8
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pres s 138 ins 2016 SL No. 46 s 3
139Restriction on introducing restricted plant into Queensland
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce a restricted plant into Queensland if the movement of the plant into Queensland is a business movement for Queensland.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, only if the inspector is satisfied the introduction of the restricted plant will not pose a significant risk of introducing pyriform scale into Queensland.(3)In this section—restricted plant means a plant of a family mentioned in schedule 12A but does not include the following—(a)the fruit of the plant;(b)cut or dried flowers;(c)foliage that has been removed from the rest of the plant for display;(d)a plant whose roots are free of soil and to which no leaves or flowers are attached.s 139 (orig s 131H) prev s 139 ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
amd 2005 SL No. 157 s 4
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
amd 2007 SL No. 19 s 9
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pres s 139 ins 2016 SL No. 46 s 3
s 140 (prev s 131I) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 10
s 141 (prev s 131J) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 10
s 142 (prev s 131K) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
amd 2004 SL No. 232 s 4
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 143 (prev s 131L) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
amd 2004 SL No. 232 s 5
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 144 (prev s 131M) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
amd 2004 SL No. 232 s 6
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 145 (prev s 131N) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 146 (prev s 131O) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 147 (prev s 131P) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
amd 2007 SL No. 19 s 11
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 148 (prev s 131Q) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 149 (prev s 131R) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
amd 2007 SL No. 19 s 12
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 150 (prev s 131S) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 151 (prev s 131T) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
s 152 (prev s 131U) ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 3
sub 2005 SL No. 157 s 5
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 9
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 3
pt hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
div hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
In this part—electric ant means the pest Wasmannia auropunctata (Roger).high risk item see section 154.pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 155.restricted area means a restricted area declared under section 162.soil includes a soil substitute that could be used as a growing medium for a plant.potting mix, organic mulchs 153 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
(1)A high risk item means any of the following—(a)a plant that has been grown, kept or harvested in a restricted area;•a pot plant that has been kept at premises in a restricted area•fruit or flowers picked in a restricted area(b)soil or a thing that has soil attached;turf(c)waste material, other than soil, that—(i)comes from the ground; or(ii)is manufactured from material that comes from the ground;material extracted from the ground as part of building construction(d)waste biosolids that are a product of processing or manufacturing an animal, a plant, or anything that comes from an animal or a plant;•solid waste from a sewage treatment plant•solid waste produced by processing an animal at an abattoir(e)a container used for growing, harvesting, moving, packing or storing that contains soil or has soil attached;beehive, bin, carton, case, crate, pallet, pot(f)baled hay or straw;(g)an appliance used—(i)to disturb soil; or(ii)for building work or construction; orformwork, scaffolding(iii)for packing or moving a thing mentioned in paragraphs (a) to (f).(2)Also, a thing is a high risk item if—(a)the thing is associated with an activity performed by a person; andExample of a thing associated with an activity—
rubbish that is put out for collection(b)an inspector—(i)decides the thing may spread electric ant; and(ii)notifies the person of the decision.s 154 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
amd 2011 SL No. 202 s 8
div hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
155Declaration of pest quarantine area
(1)The area consisting of the prescribed suburban areas, in the Cairns Regional Council’s local government area, shown on the electric ant pest quarantine area map held by the department, is declared to be a pest quarantine area for electric ant.(2)In this section—prescribed suburban areas means each of the following areas—(a)Barron;(b)Caravonica;(c)Holloways Beach;(d)Kewarra Beach;(e)MacAlister Range;(f)Machans Beach;(g)Smithfield;(h)Trinity Beach;(i)Trinity Park;(j)Yorkeys Knob.The electric ant pest quarantine area map may be inspected during business hours at the department’s office at 21–23 Redden Street, Cairns, and may also be viewed on the department’s website.s 155 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
amd 2008 SL No. 38 s 28
The objects of the quarantine for a pest quarantine area are—(a)to prevent the movement of electric ant within or out of the pest quarantine area; and(b)to eradicate electric ant in Queensland.s 156 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
div hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
sdiv 1 (s 157) ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
157Restrictions on movement within or out of pest quarantine area
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a live electric ant within or out of a pest quarantine area.sdiv 1 (s 157) ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
sdiv hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
In this subdivision—land does not include a dwelling house on the land.s 158 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
amd 2011 SL No. 202 s 9
159Obligation of owner of land to allow surveillance
(1)This section applies if an inspector requires an owner of land in a pest quarantine area to allow the inspector to carry out surveillance on the land to look for and monitor the spread of electric ant.(2)The owner must not refuse to allow the inspector to carry out the surveillance.(3)Without limiting subsection (1), an inspector may carry out surveillance on the land by putting baits, lures or traps on the land.(4)The inspector may direct the owner to remove any thing on the land that would obstruct the inspector carrying out surveillance on the land.Examples of things for subsection (4)—
rubbish, scrap metal, vegetation(5)When making the requirement or direction, the inspector must give the person an offence warning.s 159 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
160Restriction on who may treat land or things
(1)An owner of land in a pest quarantine area must not, unless directed by an inspector, treat, or allow another person, other than an inspector or an appropriate person, to treat—(a)the land; or(b)the following on the land—(i)electric ant;(ii)a plant or other thing infested with electric ant.(2)In this section—appropriate person means a person who is authorised by the chief executive.s 160 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
161Treatment of infested land or things
(1)This section applies if an inspector directs an owner of land infested with electric ant to treat, or allow an inspector to treat—(a)the land; or(b)the following on the land—(i)electric ant;(ii)a plant or other thing infested with electric ant.(2)If the owner is directed to carry out the treatment, the owner must carry out the treatment in the way directed by the inspector.(3)If the owner is directed to allow an inspector to carry out the treatment, the owner must not refuse to allow the inspector to carry out the treatment.(4)When making the direction, the inspector must give the owner an offence warning.s 161 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
div hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
sdiv hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
162Declaration of restricted area
(1)If the chief executive considers it necessary to achieve the objects of the quarantine for a pest quarantine area, the chief executive may—(a)declare an area in the pest quarantine area to be a restricted area; and(b)define the boundaries of the area so declared.(2)The chief executive must give notice of the declaration in a newspaper that is published in the Cairns Regional Council’s local government area at least 5 days a week and circulates generally in the restricted area.(3)The notice must state each of the following—(a)that an area has been declared to be a restricted area;(b)the location and boundaries of the area;(c)where a map showing the boundaries of the area is available for public inspection.s 162 ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
amd 2008 SL No. 38 s 29
sdiv 2 (ss 163–164) ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
This subdivision does not limit division 3.sdiv 2 (ss 163–164) ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
164Restrictions on movement within or out of restricted area
A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move a high risk item within or out of a restricted area.sdiv 2 (ss 163–164) ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 14
pt hdg prev pt 17 hdg ins 2007 SL No. 19 s 14
om 2007 SL No. 258 s 4
pres pt 17 hdg ins 2008 SL No. 359 s 3
In this part—mango malformation disease means a fungal disease of mango plants caused by several different species of Fusarium, including Fusarium mangiferae.mango plant means Mangifera indica L.pest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 166.s 165 prev s 165 ins 2007 SL No. 19 s 14
om 2007 SL No. 258 s 4
pres s 165 ins 2008 SL No. 359 s 3
166Declaration of pest quarantine area
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for mango malformation disease.s 166 prev s 166 ins 2007 SL No. 19 s 14
om 2007 SL No. 258 s 4
pres s 166 ins 2008 SL No. 359 s 3
The objects of the quarantine for the pest quarantine area are—(a)to prevent the introduction of mango malformation disease into the pest quarantine area; and(b)to prevent or control the spread of mango malformation disease in the pest quarantine area; and(c)to control or remove mango malformation disease in or from the pest quarantine area.s 167 prev s 167 ins 2007 SL No. 19 s 14
om 2007 SL No. 258 s 4
pres s 167 ins 2008 SL No. 359 s 3
168Restriction on introduction
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce into the pest quarantine area—(a)mango malformation disease; or(b)a mango plant, other than the fruit of a mango plant; or(c)an appliance that has been in contact with a mango plant.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, for the introduction of a thing mentioned in subsection (1) (a) to (c) only if the inspector is satisfied the introduction of the thing will not pose a significant risk of spreading mango malformation disease in the pest quarantine area.s 168 prev s 168 ins 2007 SL No. 19 s 14
om 2007 SL No. 258 s 4
pres s 168 ins 2008 SL No. 359 s 3
168ARestriction on movement within the pest quarantine area
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, move from a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area to another parcel of land in the area—(a)mango malformation disease; or(b)a mango plant that the person knows, or ought reasonably to know, is infected with mango malformation disease; or(c)an appliance that has been in contact with a mango plant the person knows, or ought reasonably to know, is infected with mango malformation disease.(2)An inspector may give an approval, with or without conditions, for the movement of a thing mentioned in subsection (1) (a) to (c) only if the inspector is satisfied the movement of the thing will not pose a significant risk of spreading mango malformation disease in the pest quarantine area.s 168A ins 2008 SL No. 359 s 3
pt hdg orig pt 18 hdg exp 2 September 2002 (see s 133)
prev pt 18 hdg ins 2010 SL No. 339 s 4
om 2011 SL No. 202 s 10
pres pt 18 hdg ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 3
In this part—at any time includes any time before the commencement of this section.CGMMV means Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus.infested plant means a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae infested with CGMMV.Examples of plants of the family Cucurbitaceae—
cucumber, melon, pumpkin, squashpest quarantine area means the pest quarantine area declared under section 170.restricted item means any of the following—(a)soil that has, or may have, come in contact at any time with infested plants;(b)an appliance that was, or may have been, used at any time in the planting, harvesting or production of plants of the family Cucurbitaceae, including, for example, harvesting bins, knives and secateurs;(c)materials that were, or may have been, used at any time for packaging plants of the family Cucurbitaceae if the packaging is or may have been for the purposes of a business movement of those plants for the pest quarantine area.s 169 prev s 169 ins 2010 SL No. 339 s 4
om 2011 SL No. 202 s 10
pres s 169 ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 3
170Declaration of pest quarantine area—Act, s 11
The whole of Queensland is declared to be a pest quarantine area for CGMMV.s 170 prev s 170 ins 2010 SL No. 339 s 4
om 2011 SL No. 202 s 10
pres s 170 ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 3
The objects of the quarantine for the pest quarantine area are—(a)to prevent the introduction of CGMMV into the pest quarantine area; and(b)to prevent the spread of CGMMV within the pest quarantine area; and(c)to control CGMMV within or remove CGMMV from the pest quarantine area.s 171 prev s 171 ins 2010 SL No. 339 s 4
om 2011 SL No. 202 s 10
pres s 171 ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 3
172Restriction on introducing and moving particular items in pest quarantine area
(1)A person must not, without an inspector’s approval, introduce the following into, or move the following within or out of, the pest quarantine area—(a)a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae, other than a fruit of a plant of that family, if the movement is a business movement for the area;(b)CGMMV (whether in existence as part of an infested plant or otherwise);(c)a restricted item.(2)An inspector may make an approval, with or without conditions, that allows a person to be exempted from subsection (1) if an introduction or movement under the approval will not pose a significant risk of introducing or spreading CGMMV.(3)A person may introduce or move a thing as mentioned in subsection (1) under an approval under subsection (2).s 172 prev s 172 ins 2010 SL No. 339 s 4
om 2011 SL No. 202 s 10
pres s 172 ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 3
amd 2016 SL No. 46 s 4
172AObligation to keep documents relating to movement
(1)This section applies to the owner of a parcel of land in the pest quarantine area if a plant of the family Cucurbitaceae, other than a fruit of a plant of that family—(a)is introduced from out of the pest quarantine area to the parcel of land under an approval mentioned in section 172 (2); or(b)is moved from the parcel of land to another parcel of land in the area or out of the area.(2)The owner of the parcel of land must keep a copy of each business document relating to the introduction or movement of the plant for at least 1 year after it is introduced or moved, unless section 11C or 11D of the Act applies to that person in relation to the business document.s 172A ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 3
amd 2016 SL No. 46 s 5
172BObligation of land owner to allow surveillance
(1)If an inspector requires an owner of land in the pest quarantine area to allow the inspector to perform surveillance, including inspection, of the land to look for and monitor the spread of CGMMV, the owner must allow the inspector to perform the surveillance.(2)Without limiting subsection (1), an inspector may perform surveillance of the land by—(a)examining a plant on the land; or(b)examining any appliance that may have come into contact at any time with an infested plant; or(c)taking, without payment, a sample of a plant or soil on the land and testing the sample, including by taking the sample to a laboratory for testing.(3)If a thing on land, other than a dwelling house or another structure affixed to the land, would obstruct the inspector performing surveillance of the land, the inspector may direct the owner of the land to move or remove the thing.(4)When making a requirement under subsection (1) or giving a direction under subsection (3), the inspector must give the person an offence warning.(5)In this section—surveillance in relation to land, does not include surveillance of a dwelling house on the land.testing, a sample of a plant, includes taking actions that may result in destroying the plant.s 172B ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 3
172CRequirement to treat plants or restricted item
(1)An inspector may give a person who is the owner of, or appears to be in charge of, land or a thing in the pest quarantine area, a written requirement—(a)to treat plants on the land or a restricted item in the area; or(b)to destroy infested plants or plants that, under section 5 of the Act, are deemed to be infested.(2)A person given a requirement under subsection (1) must comply with the requirement in the way, and at the time, stated in the requirement.(3)The requirement must include an offence warning.s 172C ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 3
ch hdg ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 11
sub 2007 SL No. 19 s 15; 2012 SL No. 224 s 12
pt hdg (prev pt 18 hdg) ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 19
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 12
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 15
ins 2012 SL No. 224 s 12
173Notification of new restrictions for restricted area
(1)This section applies if, before the commencement of this section, the chief executive declares an area to be a restricted area.(2)If the chief executive decides the amending regulation should, on or after the commencement, apply to the restricted area, the chief executive must give notice of the decision in each newspaper in which the chief executive gave notice of the declaration.(3)The notice must state the following—(a)a sufficient reference to the location of the restricted area to identify the area;(b)the day the restricted area was declared;(c)that each of the following are in addition to the information or requirements stated, under the unamended regulation, section 49 (3) in the notice of the declaration—(i)if a person is carrying on a commercial activity in the area, the circumstances under which the person is required to treat high risk items and sign a fire ant declaration;(ii)the restriction on disturbing soil in the area;(iii)the circumstances under which high risk items associated with a business person’s commercial activity must be treated and certified.(4)If the chief executive gives notice under subsection (2), the amending regulation applies to the restricted area from the day of publication, or first publication, of the notice.(5)In this section—amending regulation means the Plant Protection Amendment Regulation (No. 5) 2003.unamended regulation means this regulation as in force before the commencement.s 173 (prev s 165 (prev s 169 (orig s 132))) ins 2003 SL No. 367 s 22 (2)
renum 2006 SL No. 234 s 13; 2007 SL No. 19 s 13; 2010 SL No. 339 s 3
pt 2 (s 174) ins 2012 SL No. 224 s 13
174Notification of new restrictions for restricted area
(1)This section applies if, before the commencement of this section, the chief executive declares an area to be a restricted area for chapter 3, part 2.(2)If the chief executive decides the amending regulation should, on or after the commencement of this section, apply to the restricted area, the chief executive must give notice of the decision—(a)in each newspaper in which the chief executive gave notice of the declaration; and(b)on the department’s website.(3)The notice under subsection (2) must state the following—(a)a sufficient reference to the location of the restricted area to identify the area;(b)the day the restricted area was declared;(c)that the restricted area is—(i)a high risk restricted area; or(ii)a low risk restricted area;(d)where a map showing the boundaries of the restricted area is available for public inspection;(e)that the restrictions mentioned in sections 51 to 58, as in force after the commencement of this section, apply to the restricted area.(4)A notice under subsection (2) (a) must also state that the notice on the department’s website shows the boundaries of the restricted area.(5)A notice under subsection (2) (b) must also show the boundaries of the restricted area.(6)If the chief executive gives notice under subsection (2), the amending regulation applies to the restricted area from the day of publication, or first publication, of the notice.(7)In this section—amending regulation means the Plant Protection Amendment Regulation (No. 2) 2012 .pt 2 (s 174) ins 2012 SL No. 224 s 13
pt 3 (s 175) ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 4
175Saving of obligation to keep particular document
(1)This section applies to the owner of a parcel of land if the owner was, before the commencement, required under the Plant Protection (Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic) Quarantine Notice 2014, section 7 to keep a copy of any relevant movement document as mentioned in that section.(2)To remove doubt, it is declared that the owner’s obligation to keep the document for at least 1 year as stated in that section was not, and is not, affected even though the notice no longer remains in force.pt 3 (s 175) ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 4
Insects and mites
Common name | Scientific name and author |
African black beetle | Heteronychus arator (Fabricius) |
Argentine ant | Linepithema humile (Mayr) |
armyworm | Mythimna unipuncta Haworth |
ash whitefly | Siphoninus phillyreae (Haliday) |
Bactrocera atrisetosa | Bactrocera atrisetosa (Perkins) |
Bactrocera decipiens | Bactrocera decipiens (Drew) |
Bactrocera kirki | Bactrocera kirki (Froggatt) |
Bactrocera tau | Bactrocera tau (Walker) |
Bactrocera trilineola | Bactrocera trilineola Drew |
Bactrocera trivialis | Bactrocera trivialis (Drew) |
Bactrocera xanthodes | Bactrocera xanthodes (Broun) |
banana fruit fly | Bactrocera musae (Tryon) |
banana skipper butterfly | Erionota thrax (Linnaeus) |
banana stem weevil | Odoiporus longicollis (Oliver) |
banana weevil borer | Cosmopolites sordidus (Germar) |
Bezzi fruit fly | Bactrocera occipitalis (Bezzi) |
black carpenter ant | Camponotus pennsylvanicus (De Geer) |
boll weevil | Anthonomus grandis Boheman |
breadfruit fruit fly | Bactrocera umbrosa (Fabricius) |
Californian red scale | Aonidiella aurantii (Maskell) |
carambola fruit fly | Bactrocera carambolae Drew and Hancock |
Chinese fruit fly | Bactrocera minax (Enderlein) |
citrus blackfly | Aleurocanthus woglumi Ashby |
citrus fruit borer | Citripestis sagitiferella (Moore) |
citrus gall wasp | Bruchophagus muli (Boucek and Brough) |
citrus psyllid | Diaphorina citri Kuw. |
citrus red mite | Panonychus citri (McGregor) |
cocoa pod borer | Conopomorpha cramerella (Snellen) |
codling moth | Cydia pomonella (Linnaeus) |
coffee berry borer | Hypothenemus hampei (Ferrari) |
coffee mealybug | Planococcus lilacinus (Cockerell) |
Colorado potato beetle | Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say) |
Cook Islands fruit fly | Bactrocera melanotus (Coquillett) |
cotton boll weevil | Anthonomus grandis Boheman |
cucumber fly | Bactrocera cucumis (French) |
cut worm | Agrotis interjectionis (Guenée) |
Dacus bivattatus | Dacus bivattatus (Bigot) |
Dacus ciliatus | Dacus ciliatus Loew |
electric ant | Wasmannia auropunctata (Roger) |
Erythrina gall wasp | Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim |
European corn borer | Pyrausta nubilalis (Hübner) |
European flower thrips | Thrips vulgatissimus Haliday |
European red mite | Panonychus ulmi (Koch) |
European wasp | Vespula germanica (Fabricius) |
false codling moth | Cryptophlebia leucotreta (Meyrick) |
Fijian fruit fly | Bactrocera passiflorae (Froggatt) |
granary weevil | Sitophilus granarius (Linnaeus) |
grape leaf-folder | Desmia funeralis (Hübner) |
grape leafhopper | Erythroneura elegantula Osborn |
grape Phylloxera Type B | Daktulosphaira vitifolii (Fitch) |
grape thrips | Drepanothrips reuteri Uzel |
grasshoppers and locusts | Acrididae |
guava fruit fly | Bactrocera correcta (Bezzi) |
hessian fly | Mayetiola destructor (Say) |
Indian fruit fly | Bactrocera caryeae (Kapoor) |
Jack Beardsley mealybug | Pseudococcus jackbeardsleyi Gimpel & Miller |
Japanese bayberry whitefly | Parabemisia myricae (Kuwana) |
Japanese beetle | Popillia japonica Newmann |
Japanese citrus fruit fly | Bactrocera tsuneonis (Miyake) |
khapra beetle | Trogoderma gladrum (Herbst) |
khapra beetle | Trogoderma granarium Everts |
khapra beetle | Trogoderma inclusum Le Conte |
large grain borer | Prostephanus truncates (Horn) |
lettuce aphid | Nasonovia ribisnigri (Mosley) |
mango fruit borer | Citripestis eutraphera (Meyrick) |
mango leaf gall midge | Procontarinia spp. |
mango leafhopper | Idioscopus clypealis (Lethierry) |
mango leafhopper | Idioscopus nitidulus (=niveosparsus) (Walker) |
mango pulp weevil | Sternochetus frigidus (Fabricius) |
mango seed weevil | Sternochetus mangiferae (Fabricius) |
Mediterranean fruit fly | Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) |
melon fly | Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) |
melon thrips | Thrips palmi Karny |
Mexican fruit fly | Anastrepha ludens (Loew) |
Navel orangeworm | Amyelois transitella Walker |
New Zealand flower thrips | Thrips obscuratus (Crawford) |
omnivorous leafroller | Platynota sultana Walsingham |
Oriental fruit fly | Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) |
Pacific spider mite | Eotetranychus willamettei (McGregor) |
palm leaf beetle | Brontispa longissima (Gestro) |
papaya fruit fly | Bactrocera papayae Drew and Hancock |
peach fruit fly | Bactrocera zonata (Saunders) |
pea leafminer | Liriomyza huidobrensis (Blanchard) |
pear fruit moth | Numonia pirivorella (Matsumura) |
Philippine fruit fly | Bactrocera philippinensis Drew and Hancock |
pink bollworm | Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) |
pinkspotted bollworm | Pectinophora scutigera (Holdaway) |
plum weevil or plum curculio | Conotrachelus nenuphar (Herbst) |
poinsettia whitefly or silverleaf whitefly | Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (biotype B) (= B. argentifolii Bellows and Perring) |
potato moth | Phthorimaea operculella (Zeller) |
pyriform scale | Protopulvinaria pyriformis (Cockerell) |
Queensland fruit fly | Bactrocera tryoni (Froggatt) |
red banded mango caterpillar | Deanolis sublimbalis (Snellen) |
red imported fire ant | Solenopsis invicta Buren |
rice water weevil | Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel |
rice weevil | Sitophilus oryzae (Linnaeus) |
rough strawberry weevil | Otiorhynchus rugosostriatus (Goeze) |
Russian wheat aphids | Diuraphis noxia (Mordvilko) |
rust red flour beetle | Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) |
serpentine leafminer | Liriomyza trifolii (Burgess) |
solanum fruit fly | Bactrocera latifrons (Hendel) |
South African citrus thrips | Scirtothrips aurantii Faure |
spider mite | Tetranychus piercei McGregor |
spiraling whitefly | Aleurodicus dispersus Russell |
Sri Lankan fruit fly | Bactrocera kandiensis Drew and Hancock |
stem borer | Chilo spp. |
strawberry bud weevil | Anthonomus bisignatus Schenkling |
strawberry tortrix | Acleris comariana Lienig and Zeller |
sugarcane borer | Scirpophaga spp. |
sugarcane borer | Sesamia spp. |
sugarcane borer | Tetramoera schistanceana (Snellen) |
sugarcane leafhopper | Eumetopina spp. |
sugarcane leafhopper | Pyrilla perpusilla (Walker) |
sugarcane planthopper | Perkinsiella spp. |
sugarcane scale | Aulacaspis tegalensis (Zehntner) |
sugarcane weevil borer | Rhabdoscelus obscurus (Boisduval) |
sugarcane whitefly | Aleurolobus barodensis (Maskell) |
sugarcane woolly aphid | Ceratovacuna lanigera Zehntner |
summer fruit tortrix | Adoxophyes orana Fischer von Rösslerstamm |
tobacco beetle | Lasioderma serricorne (Fabricius) |
tobacco stem borer | Scrobipalpa heliopa (Lower) |
Tongan fruit fly | Bactrocera facialis (Coquillett) |
tropical fire ant | Solenopsis geminata (Fabricius) |
variegated cutworm | Peridroma saucia (Hebner) |
variegated grape leafhopper | Erythroneura variabilis Beamer |
vegetable leafminer | Liriomyza sativae Blanchard |
warehouse beetle | Trogoderma variabile Ballion |
western flower thrips | Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) |
western grapeleaf skeltonizer | Harrisiana brillians Barnes and McDunnough |
woolly whitefly | Aleurothrixus floccosus (Maskell) |
Molluscs
Common name | Scientific name and author |
giant African snail | Achatina fulica Bowditch |
golden apple snail | Pomacea canaliculata (Lamark 1819) |
green snail | Helix aperta (Born) |
A OrganismsNematodesBursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner and Buhrer) NickleDitylenchus destructor ThorneGlobodera pallida (Stone) Behrens (abbreviated name—potato cyst nematode)Globodera rostochiensis (Wollenweber) Behrens (abbreviated name—golden nematode)Heterodera avenae (Wollenweber) FilipjevHeterodera glycines IchinohePratylenchus coffeae (Zimmermann) Filipjev and Schuurmans StekhovenPratylenchus goodeyi Sher and AllenRhadinaphelenchus cocophilus (Cobb) GoodeyXiphinema index Thorne and AllenPlantsA plant of the genera Musa spp., other than—(a)a plant that produces edible fruit; or(b)an indigenous plant that is not a volunteer plant.Berberis spp.Ensete spp.Mahonia spp.Orobanche ramosa L. (common name—branched broomrape)Striga asiatica (L.) KuntzePhytoplasmasapple chat fruit phytoplasmaapple proliferation phytoplasmaapple rubbery wood phytoplasmaapricot chlorotic leaf roll phytoplasmaapricot witches broom phytoplasmaAustralian grapevine yellows phytoplasmacherry albino (X disease) phytoplasmacherry necrotic rusty mottle phytoplasmacherry western X (peach X) phytoplasmaEuropean stone fruit yellows phytoplasmagrapevine flavesence doree phytoplasmalittle cherry phytoplasmalittle peach phytoplasmapalm lethal yellowing phytoplasmaParry’s disease (pear) phytoplasmapeach chlorotic leaf roll phytoplasmapeach red suture phytoplasmapeach rosette phytoplasmapeach X phytoplasma (including peach eastern X phytoplasma)peach yellows phytoplasmapear decline phytoplasmaplum chlorotic leaf roll phytoplasmasugarcane grassy shoot phytoplasmasugarcane white leaf phytoplasma (White leaf)BacteriaAcidovorax avenae subsp. avenae (Manns) Willems et al.Agrobacterium tumefaciens biovar 3 (E.F. Smith and Town.)Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus (Spiek and Kotth.) Davies et al.Erwinia amylovora (Burrill) Winslow et al. (abbreviated name—fire blight)Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli (Davies et al.) Evtushenko“Liberobacter asiatica” Jagoueix et al.Panotoea stewartii subsp. stewartii (E.F. Smith) Mergaert et al.Pseudomonas angulata (Fromme and Murray) Holland“Pseudomonas celebensis”= banana blood disease bacterium (uncharacterised)Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola (Burkeholder) Young et al.Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Van HallPseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci (Wolf and Foster) Young et al.Pseudomonas syzygii I. Roberts et al.Ralstonia solanacearum (E.F. Smith) Yabuuchi et al.Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) DowsonXanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri (Hasse) VauterinXanthomonas axonopodis pv. malvacearum (E. F. Smith) DowsonXanthomonas axonopodis pv. vasculorum (Cobb) DyeXanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Pammel) DowsonXanthomonas campestris pv. oryzae (Ishiyama) Swings et al.Xanthomonas campestris pv. phaseoli (E. F. Smith) DyeXanthomonas campestris pv. vasculorum (Cobb)Xanthomonas fragariae J.K. Kennedy and KingXanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola (Ishiyama) Swings et al.Xylella fastidiosa Wells et al.Xylophilus ampelinus (Panagopoulos) Willems et al.FungiAlbugo candida (Pers.) Kuntze (abbreviated name—white blister of brassica)Anisogramma anomala (Peck) E. Müll. (1962)Apiosporina morbosa (Schwein.) Arx (1954)Ascochyta rabiei (Pass.) Labr.Asperisporium caricae (Speg.) Maubl.Ceratocystis ulmi (Buisman) C. Moreau (1952)Cercospora longipes E.J. ButlerCiborinia camelliae L.M. Kohn (1979)Claviceps africana Freder., Mantle and De MillianoClaviceps gigantea S.F. Fuentes, Isla, Ullstrup and RodriquezClaviceps sorghi P. Kulkarni, Seshadri and HedgeColeosporium ipomoeae (Schwein.) BurrillColletotrichum kahawae J.M. Waller and P.D. BridgeColletotrichum lindemuthianum (Sacc. and Magnus) Scribm.Cryphonectria cubensis (Bruner) HodgesCryphonectria parasitica (Murrill) M.E. Barr (1978)Deuterophoma tracheiphila PetriElsinoe fawcettii Bitanc. and JenkinsEutypa lata (Pers.:Fr.) Tul. and C. Tul.Exobasidium vexans MasseeFusarium moniliforme J. Sheld. var. subglutinans Wollenw. and ReinkingFusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f.sp. chrysanthemi G.M. Armstrong, J.K. Armstrong and R.H. LittrellFusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f. sp. cubense (E.F. Smith) W.C. Snyder and H.N. Hansen. race 1, race 2, subtropical race 4 or tropical race 4Fusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f.sp. lycopersici (Sacc.) W.C. Snyder and H.N. HansenFusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f.sp. vasinfectum (Atk.) W.C. Snyder and H.N. HansenGuignardia bidwellii (Ellis) Viala and RavazGuignardia citricarpa Kiely (anamorph Phyllosticta citricarpa (McAlpine) Aa)Gymnosporangium R. Hedw.Hemileia vastatrix Berk. and BroomeMagnaporthe grisea (T.T. Hebert) M.E. Barr (1977)Microbotryum violaceum (Pers.:Pers.) G. Deml. and OberwinklerMonilinia fructigena Honey in Whetzel (1946)Mycosphaerella angulata W.A. Jenkins (anamorph Cercospora brachypus Ellis and Everh.)Mycosphaerella fijiensis M. Morelet (anamorph Paracercospora fijiensis (M. Morelet) Deighton)Mycosphaerella musae (Speg.) Syd. and P. Syd.Mycosphaerella musicola J.L. Mulder (anamorph Pseudocercospora musae (Zimm.) Deighton)Pachymetra chaunorhiza B.J. Croft and M.W. DickPeronosclerospora maydis (Racib.) C.G. ShawPeronosclerospora philippinensis (W. Weston) C.G. ShawPeronosclerospora sacchari (T. Miyake) Shirai and K. HaraPeronosclerospora sorghi (W. Weston and Uppal) C.G. ShawPeronosclerospora spontanea (W. Weston) C.G. ShawPeronospora hyoscyami de BaryPhakospora euvitis Y. Ono (2000)Phoma tracheiphila (Petri) L.A. Kantsch. and Gokaschvili (1948)Phymatotrichopsis omnivora (Duggar) HennebertPhymatotrichum omnivorum Duggar (1916)Physopella ampelopsidis (Dietel and P. Syd.) Cummins and RamacharPhytophthora cinnamomi RandsPhytophthora fragariae var. fragariae HickmanPhytophthora ramorum Werres, De Cock and Man in 't VeldPlasmodiophora brassicae WoroninPlasmopara halstedii (Farl.) Berl. and DeToniPseudopezicula tetraspora Korf, R.C. Pearson and ZhuangPseudopezicula tracheiphila (Müller-Thurg.) Korf and Zhuang (anamorph Phialophora tracheiphila (Sacc. and D. Sacc.) Korf)Puccinia asparagi D.C. (1805)Puccinia horiana Henn.Puccinia psidii sensu latoPyricularia oryzae CavaraRoesleria subterranea (Weinm.) Redhead (1985)Rosellinia necatrix Berl. ex Prill. (1904)Sclerospora graminicola (Sacc.) J. Schröt.Sphaceloma arachidis Bitanc. and JenkinsSporisorium cruentum (Kühn) K. VánkyStagnospora saccharum T.T. Lo and L. Ling (1950)Synchytrium endobioticum (Schilb.) PercivalTilletia barclayana (Bref.) Sacc. and P. Syd. (1899)Tilletia indica MitraUredo rangelii (J.A. Simpson, K. Thomas and C.A. Grgurinovic)Uromyces gladioli Henn.Uromyces transversalis (Thüm.) G. WinterUstilago scitaminea Syd. (abbreviated name—sugarcane smut)Verticillium dahliae Kleb. (1913)
B Viruses and viroidsVirusesApple chlorotic leaf spot virusapple flat limb virus (uncharacterised)Apple mosaic virusapple ringspot virus (uncharacterised)apple rough skin virus (uncharacterised)apple star crack virus (uncharacterised)apricot ring pox virus (uncharacterised)Arabis mosaic virusArtichoke Italian latent virusBanana bract mosaic virus (abbreviated name—banana bract mosaic)Banana bunchy top virus (abbreviated name—banana bunchy top)Banana streak virus (abbreviated name—banana streak)Begomovirus Cotton leaf curl virusbratislava mosaic virus (uncharacterised)cherry black canker virus (uncharacterised)Cherry rasp leaf virusCitrus tristeza virusCucumber green mottle mosaic virusCucumber mosaic virus (abbreviated name—cucumber mosaic)grapevine Ajinashika virus (uncharacterised)Grapevine Algerian latent virusGrapevine Bulgarian latent virusGrapevine chrome mosaic virusgrapevine corky bark virus (uncharacterised)grapevine enation virus (uncharacterised)Grapevine fanleaf virusgrapevine fleck virus (uncharacterised)Grapevine leafroll virusGrapevine virus AGrapevine virus BGrapevine virus DGrapevine yellow vein virusHigh plains virusMaize dwarf mosaic virusMyrobalan latent ringspot virusNepovirus Cherry leaf roll virus (blackline)Papaya ringspot virus type P (abbreviated name—papaya ringspot)Papaya ringspot virus type W (abbreviated name—papaya ringspot)Peach rosette mosaic virusPeach wart virus (uncharacterised)Peanut stripe virusPea seed-borne mosaic virusPlum pox virusprune diamond canker virus (uncharacterised)Prune dwarf virusPrunus necrotic ringspot virusSorghum mosaic virusSquash mosaic virusSugarcane bacilliform virusSugarcane Fiji disease virusSugarcane mosaic virussugarcane Ramu stunt virussugarcane streak mosaic virus (Potyviridae)Sugarcane streak virussugarcane striate mosaic associated virus (uncharacterised)Tobacco mosaic virusTobacco ringspot virusTomato black ring virusTomato leaf curl virusTomato mosaic virusTomato ringspot virusTomato yellow leaf curl virusWatermelon mosaic virusWheat spindle streak mosaic virusWheat streak mosaic virusZucchini yellow mosaic virusViroidsApple scar skin viroidAvocado sunblotch viroidChrysanthemum stunt viroidCitrus exocortis viroidCoconut cadang-cadang viroidDapple apple viroidgrapevine stem pitting viroid (uncharacterised)grapevine summer mottle viroid (uncharacterised)grapevine vein necrosis viroid (uncharacterised)Grapevine yellow speckle viroid-1Grapevine yellow speckle viroid-2Potato spindle tuber viroid
C DisordersAdditional information about the disorders listed in part 2, item C of this schedule
Disorder Description bacterial wilt an occlusion and necrosis of the xylem tissue associated with invasion by plant pathogenic bacteria banana freckle freckle disease of banana, associated with either of the following genera of fungi that are pathogenic to plants or bananas— (a) Guignardia spp.;(b) Phyllosticta spp., other than Phyllosticta maculata M.H. Wong & Crous.blight a necrosis of leaf or stem tissue, with sudden onset, associated with a plant pathogenic bacterium (bacterial blight) or fungus (fungal blight) canker a sharply delineated necrosis or suberisation of the cortical tissue of leaves or stems, associated with a plant pathogenic bacterium or fungus downy mildew a necrosis or organoid gall of leaf or stem tissue associated with intercellular hyphae and emergent sporophores of a fungus of the family Peronosporaceae ergot an organoid gall of floral and ovule tissue associated with intercellular and extracellular hyphae and emergent sporophores of a fungus of the genus Claviceps Tul., order Hypocreales fusarium wilt an occlusion and necrosis of the xylem tissue, associated with plant pathogenic strains of a fungus of the genus Fusarium Link ex Fr., order Moniliales gall a swelling of tissue resulting from multiplication of cells (histoplasia), enlargement of cells (hypertrophy) or replacement with tissue of another organism, and associated with an intracellular or intercellular fungus, bacterium, phytoplasma, virus or mite grey mould a necrosis of leaf, stem or floral tissue associated with intercellular and extracellular hyphae or emergent sporophores of a fungus of the genus Botrytis Pers. ex Fr., order Moniliales, or Sclerotinia Fuckel, order Helotiales mango malformation an abnormal development of vegetative shoots and inflorescences of a mango plant, caused by several different species of Fusarium, including Fusarium mangiferae mosaic (mottles or yellows) a uniform or patchy variation of normal green colour associated with intracellular phytoplasm, virus or viroid infection mutant plant a plant with recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) acquired artificially or by natural transmission but having an undesired quality of increasing the weed potential of the plant or interfering with pest management programs powdery mildew a necrosis or suberisation of leaf or stem tissue associated with intracellular and extracellular hyphae and sporophores of a fungus of the order Erysiphales rust an organoid gall of leaf or stem tissue associated with intercellular hyphae, aeciospores, uredospores or teliospores of a fungus of the order Pucciniales smut an organoid gall of leaf, stem, floral or meristematic tissue associated with intercellular hyphae and chlamydospores of a fungus of the order Ustilaginales spot a localised necrosis or yellowing of leaf or stem tissue, associated with a plant pathogenic bacterium, fungus or virus white blister an organoid gall of leaf or stem tissue associated with intercellular hyphae, sporeangia, zoospores and oospores of a fungus of the genus Albugo, order Peronosporales witches broom a gall resulting in massed outgrowths of vegetative buds and associated with an intracellular or intercellular fungus, bacterium, phytoplasma, virus or mite
1For bacterial wilt, mosaic (mottles or yellows) and witches broom, the description’s reference is Plant Pathologist’s Pocketbook, CAB, Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey, UK.
2For all other disorders, apart from mutant plant, the description’s reference is Ainsworth and Bisby’s Dictionary of the Fungi, CAB, Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey, UK.
sch 1 amd 2003 SL No. 22 s 3; 2003 SL No. 158 s 3; 2004 SL No. 45 s 3; 2004 SL No. 204 s 4; 2006 SL No. 171 s 4; 2006 SL No. 234 s 15; 2007 SL No. 19 s 16; 2008 SL No. 359 s 4; 2008 SL No. 400 s 3; 2009 SL No. 149 s 6; 2010 SL No. 339 s 5; 2011 SL No. 202 s 11; 2012 SL No. 5 s 3; 2013 SL No. 32 s 21; 2013 SL No. 66 s 4; 2013 SL No. 80 s 20; 2013 SL No. 141 s 3; 2013 SL No. 143 s 3; 2013 SL No. 193 s 15; 2015 SL No. 5 s 5; 2016 SL No. 46 s 6
Insects and mites
Common name | Scientific name and author |
armyworm | Mythimna unipuncta Haworth |
banana skipper butterfly | Erionota thrax (Linnaeus) |
boll weevil | Anthonomus grandisBoheman |
citrus psyllid | Diaphorina citri Kuw. |
coffee berry borer | Hypothenemus hampei (Ferrari) |
coffee mealybug | Planococcus lilacinus (Cockerell) |
Colorado potato beetle | Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say) |
electric ant | Wasmannia auropunctata (Roger) |
false codling moth | Cryptophlebia leucotreta (Meyrick) |
grape Phylloxera Type B | Daktulosphaira vitifolii (Fitch) |
hessian fly | Mayetiola destructor (Say) |
Jack Beardsley mealybug | Pseudococcus jackbeardsleyi Gimpel & Miller |
khapra beetle | Trogoderma granarium Everts |
lettuce aphid | Nasonovia ribisnigri (Mosley) |
mango leafhopper | Idioscopus clypealis (Lethierry) |
mango leafhopper | Idioscopus nitidulus (= niveosparsus) (Walker) |
mango pulp weevil | Sternochetus frigidus (Fabricius) |
melon fly | Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) |
Navel orangeworm | Amyelois transitella Walker |
Oriental fruit fly | Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) |
papaya fruit fly | Bactrocera papayae Drew and Hancock |
pear fruit moth | Numonia pirivorella (Matsumura) |
Philippine fruit fly | Bactrocera philippinensis Drew and Hancock |
plum weevil or plum curculio | Conotrachelus nenuphar (Herbst) |
pyriform scale | Protopulvinaria pyriformis (Cockerell) |
red banded mango caterpillar | Deanolis sublimbalis (Snellen) |
red imported fire ant | Solenopsis invicta Buren |
rice water weevil | Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel |
rough strawberry weevil | Otiorhynchus rugosostriatus (Goeze) |
Russian wheat aphid | Diuraphis noxia (Mordvilko) |
rust red flour beetle | Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) |
South African citrus thrips | Scirtothrips aurantii Faure |
spider mite | Tetranychus piercei McGregor |
strawberry bud weevil | Anthonomus bisignatus Schenkling |
strawberry tortrix | Acleris comariana Lienig and Zeller |
sugarcane borer | Sesamia spp. |
sugarcane whitefly | Aleurolobus barodensis (Maskell) |
summer fruit tortrix | Adoxophyes orana Fischer von Rösslerstamm |
tropical fire ant | Solenopsis geminata (Fabricius) |
variegated cutworm | Peridroma saucia (Hebner) |
vegetable leafminer | Liriomyza sativae Blanchard |
Molluscs
Common name | Scientific name and author |
golden apple snail | Pomacea canaliculata (Lamark 1819) |
A OrganismsNematodesGlobodera pallida (Stone) Behrens (abbreviated name—potato cyst nematode)Globodera rostochiensis (Wollenweber) Behrens (abbreviated name—golden nematode)BacteriaClavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus (Spiek and Kotth.) Davies et alErwinia amylovora (Burrill) Winslow et al (abbreviated name—fire blight)“Liberobacter asiatica” Jagoueix et al“Pseudomonas celebensis”= banana blood disease bacterium (uncharacterised)Ralstonia solanacearum (E.F. Smith) Yabuuchi et alXanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri (Hasse) VauterinXanthomonas axonopodis pv. malvacearum (E. F. Smith) DowsonXanthomonas fragariae J.K. Kennedy and KingXylella fastidiosa Wells et alFungiAnisogramma anomala (Peck) E. Müll. (1962)Apiosporina morbosa (Schwein.) Arx (1954)Ceratocystis ulmi (Buisman) C. Moreau (1952)Ciborinia camelliae L.M. Kohn (1979)Cryphonectria parasitica (Murrill) M.E. Barr (1978)Fusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f. sp. cubense (E.F. Smith) W.C. Snyder and H.N. HansenGuignardia bidwellii (Ellis) Viala and RavazMagnaporthe grisea (T.T. Hebert) M.E. Barr (1977)Monilinia fructigena Honey in Whetzel (1946)Mycosphaerella fijiensis M. Morelet (anamorph Paracercospora fijiensis (M. Morelet) Deighton)Peronosclerospora sacchari (T. Miyake) Shirai and K. HaraPhakopsora euvitis Y. Ono (2000)Phoma tracheiphila (Petri) L.A. Kantsch. and Gokaschvili (1948)Phymatotrichum omnivorum Duggar (1916)Phytophthora fragariae var. fragariae HickmanPhytophthora ramorum Werres, De Cock and Man in 't VeldPuccinia asparagi D.C. (1805)Roesleria subterranea (Weinm.) Redhead (1985)Rosellinia necatrix Berl. ex Prill. (1904)Stagonospora saccharum T.T. Lo and L. Ling (1950)Tilletia barclayana (Bref.) Sacc. and P. Syd. (1899)Tilletia indica MitraUstilago scitaminea Syd.Verticillium dahliae Kleb. (1913)PlantsA plant of the genera Musa spp., other than—(a)a plant that produces edible fruit; or(b)an indigenous plant that is not a volunteer plant.Ensete spp.Orobanche ramosa L. (branched broomrape)Striga asiatica (L.) KuntzePhytoplasmasEuropean stone fruit yellows phytoplasmapeach X phytoplasma (including peach eastern X phytoplasma)sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma (White leaf)
B Viruses and viroidsVirusesBanana bract mosaic virusBanana bunchy top virusBegomovirus Cotton leaf curl virusCucumber green mottle mosaic virusNepovirus Cherry leaf roll virus (blackline)Plum pox virusSugarcane Fiji disease virussugarcane Ramu stunt virussugarcane streak mosaic virus (Potyviridae)Wheat spindle streak mosaic virusViroidsPotato spindle tuber viroid
C Disorders
Disorder Description Common or abbreviated names bacterial wilt of banana plants bacterial wilt, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by— • Ralstonia solanacearum (E. F. Smith) Yabuuchi et al; or• “Pseudomonas celebensis”= banana blood disease bacterium (uncharacterised); orbacterial wilt of bananasbanana blood diseasebanana bugtok diseasebanana moko disease bacterial wilt of grape plants bacterial wilt, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Xylella fastiodiosa Wells et al Pierce’s disease banana freckle freckle disease of banana, associated with either of the following genera of fungi that are pathogenic to plants or bananas— (a) Guignardia spp.;(b) Phyllosticta spp., other than Phyllosticta maculata M.H. Wong & Crous.banana freckle blight of potato plants blight, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus (Spiek and Kotth.) Davies et al. potato ring rot blight of regulated fire blight host plants blight, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Erwinnia amylovora (Burrill) Winslow et al (abbreviated name—fire blight) fire blight canker of citrus plants canker, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri (Hasse) Vauterin citrus canker downy mildew of sugarcane plants downy mildew, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Peronosclerospora sacchari (T. Miyake) Shirai and K. Hara sugarcane downy mildew fusarium wilt of banana plants fusarium wilt, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Fusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f. sp. cubense (E.F. Smith) W.C. Snyder and H.N. Hansen, race 1, race 2, subtropical race 4 or tropical race 4 fusurial wilt of bananabanana Panama disease mango malformation mango malformation disease, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by several different species of Fusarium, including Fusarium mangiferae mango malformation disease mosaic (mottles or yellows) of banana plants— banana bract mosaic disease mosaic (mottles or yellows), as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Banana bract mosaic virus (abbreviated name—banana bract mosaic) banana bract mosaic disease mosaic (mottles or yellows) of banana plants— banana bunchy top virus mosaic (mottles or yellows), as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Banana bunchy top virus (abbreviated name—banana bunchy top) banana bunchy top disease mosaic (mottles or yellows) of citrus plants mosaic (mottles or yellows), as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by “Liberobcter asiatica” Jagouix et al. citrus greeningHuanglongbing mosaic (mottles or yellows) of stonefruit plants mosaic (mottles or yellows), as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by plum pox virus plum pox virus mosaic (mottles or yellows) of sugarcane plants mosaic (mottles or yellows), as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by sugarcane Fiji disease virus sugarcane Fiji diseaseFiji virus smut of prescribed cereal crop plants smut, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Tilletia indica Mitra Karnal bunt smut of sugarcane plants smut, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Ustilago scitaminea Syd. (abbreviated name—sugarcane smut) sugarcane smut spot of banana plants spot, as described in schedule 1, part 2, under the heading ‘C Disorders’, caused by Mycosphaerella fijiensis M. Morelet (anamorph Paracercospora fijiensis (M. Morelet) Deighton) banana black Sigatoka diseasespot
sch 2 amd 2004 SL No. 204 s 5; 2006 SL No. 234 s 16; 2007 SL No. 19 s 17; 2008 SL No. 134 s 4; 2008 SL No. 359 s 5; 2008 SL No. 400 s 4; 2010 SL No. 339 s 6; 2011 SL No. 202 s 12; 2013 SL No. 32 s 22; 2013 SL No. 66 s 5; 2013 SL No. 143 s 4; 2013 SL No. 193 s 16; 2015 SL No. 5 s 6; 2016 SL No. 46 s 7
Schedule 3 Pest quarantine areas for pests of banana plants other than tropical race 4 or banana freckle
sch 3 sub 2008 SL No. 38 s 30
amd 2013 SL No. 32 s 23; 2013 SL No. 193 s 6
section 24 (2)
Blue Java
Bluggoe
Ducasse
FHIA 01 (Goldfinger)
FHIA 02
Goly Goly Pot Pot
Kluai Namwa Khom (Dwarf Ducasse)
Pisang Ceylan (Mysore type)
Sh 3436
Simoi
Tu–8
War War
Yangambi Km5
Blue Java
Bluggoe
Ducasse
FHIA 01 (Goldfinger)
Kluai Namwa Khom
Lady Finger
Pisang Ceylan (Mysore type)
1Treatment method A•remove the plant, including the corm, suckers and pseudostem from the soil•cut each pseudostem into pieces no more than 60cm long and split each piece lengthwise•cut the corm into pieces no more than 5cm in diameter
2Treatment method B•remove the fruit from the plant or spray the fruit with a registered agricultural marker dye to make it unsuitable for human or animal consumption•inject each pseudostem at a height of 30cm above the ground with 15ml of a 1% solution of 2,4-D
3Treatment method C•remove the fruit from the plant or spray the fruit with a registered agricultural marker dye to make it unsuitable for human or animal consumption•inject each pseudostem at a height of 30cm above the ground with 15ml of a 3.6% solution of glyphosate
4Treatment method D•remove the plant, including the corm, suckers and pseudostem from the soil•cut the pseudostem and leaf tissue, other than leaf tissue that is dead or not green in colour, into pieces no more than 60cm long•cut the corm, suckers and butt of each pseudostem into pieces no more than 5cm in diameter•leave the pseudostem and leaf tissue pieces to rot on the surface of the soil or bury them under at least 60cm of soil•leave the pieces of the corm, suckers and butt of each pseudostem to rot on the surface of the soil or bury them under at least 1m of soil
sch 5 amd 2013 SL No. 80 s 21
section 30 (4)
Blue Java
Bluggoe
Ducasse
FHIA 01 (Goldfinger)
FHIA 02
FHIA 25
Kluai Namwa Khom (Dwarf Ducasse)
Pisang Ceylan (Mysore type)
SH 3436
Simoi
Tu–8
Yangambi Km5
section 65, definition regulated fire blight host plant
Hybrid | Common name |
Rubus hybrids | thornless blackberry |
Species | Common name |
Prunus salicina | plum |
Rubus ideus | red raspberry |
Genus | Examples of common names |
Amelanchier | service berry, June berry |
Cotoneaster | cotoneaster |
Crataegus | hawthorn |
Cydonia | quince |
Eriobotrya | loquat |
Malus | apple |
Mespilus | medlar |
Pyracantha | fire thorn |
Pyrus | pear |
Sorbus | mountain ash |
Stransvaesia | – |
sch 7A ins 2008 SL No. 38 s 31
section 86, definition host plant
Common name | Scientific name and author |
abiu | Pouteria caimito (Ruiz and Pavon) Radlk. [Sapotaceae] |
acerola | Malpighia glabra (L.) [Malpighiaceae] M.glabra x M.punicifolia (L.) (Barbados cherry) |
akee | Blighia sapida K.Konig [Spaindacea] |
akia | Wikstroemia phillyreifolia Gray [Thymelaeaceae] |
almond (with husk) | Prunus amygdalus Batsch => Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A. Webb |
apple | Malus domestica Borkh L. [Rosaceae] Malus sylvestris Mill. [Rosaceae] (crab apple) |
apricot | Prunus armeniaca L. [Rosaceae] |
Barbados cherry | Malpighia punicifolia (L.) [Malpighiaceae] |
blackberry | Rubus fruiticosus L. [Rosaceae] |
black sapote | Diospyros ebenum J. König ex Retz. [Ebanaceae] |
black walnut | Juglans nigra L. [Juglandaceae] |
blueberry | Vaccinium corymbosum L. [Ericaceae] |
bourbon orange | Ochrosia elliptica Labill. [Apocynaceae] |
boxthorn | Lycium europaeum L. [Solanaceae] |
Brazil cherry | see Grumichama |
breadfruit | Artocarpus altilis (Parkinsonia) Fosb. [Moraceae] |
calamondin orange | Citrofortunella mitis (Blanco) J. Ingram and H. Moore [Rutaceae] |
camito (star cherry) | Chrysophyllum cainito L. [Sapotaceae] |
Cape gooseberry | Physalis peruviana L. [Solanaceae] |
capsicum | Capsicum annuum L. var. grossum (L.) sendt [Solanaceae] |
carambola (star fruit) | Averrhoa carambola L. [Oxalidaceae] |
cashew apple | Anacardium occidentale L. [Anacardiaceae] |
casimiroa (white sapote) | Casimiroa edulis LaLave and Lex. [Rutaceae] |
cherimoya | Annona cherimolia Mill. [Annonaceae] |
cherry | Prunus avium L. (sour cherry) [Rosaceae] Prunus avium L. (sweet cherry) [Rosaceae] |
chilli | Capsicum annuum v acuminatum Fingerh. [Solanaceae] (chillies) Capsicum annuum v cerasiforme (Miller) Irish [Solanaceae] (cherry peppers) Capsicum annuum v conoides (Miller) Irish [Solanaceae] (tabasco) |
citron | Citrus medica L. [Rutaceae] |
coffee berry | Coffea arabica[Rubiaceae] (Arabian coffee) Coffea canephora Pierre and froehner [Rubiaceae] Coffea excelsa Chiov. [Rubiaceae] (excelsa coffee) Coffea liberica Hiern. [Rubiaceae] (Liberian coffee) Coffea robusta Linden [Rubiaceae] (robusta coffee) |
custard apple | Annona squamosa L. x A.cherimolia Mill. [Annonaceae] |
date | Phoenix dactylifera L. [Arecaceae] |
eggplant | Solanum melongena L. [Solanaceae] |
feijoa | Acca sellowiana (Berg.) Burret [Myrtaceae] |
fig | Ficus carica L. [Moraceae] |
granadilla | Passiflora quadrangularis L. [Passifloraceae] |
grape | Vitis labrusca L. [Vitaceae] (Isabella grape) Vitis vinifera L. [Vitaceae] (wine grape) |
grapefruit | Citrus paradisi Macf. [Rutaceae] |
grumichama | Eugenia braziliensis Lam. [Myrtaceae] |
guava | Psidium guajava L. [Myrtaceae] P. littorale Raddi syn => p.cattleianum Sabine [Myrtaceae] (strawberry guava) P. cattleianum Sabine var. guineense Sw. [Myrtaceae] (Brazilian guava) P. cattleianum Sabine var. lucidum[Myrtaceae] (yellow cattley guava) P. friedrichsthalianum Nied. [Myrtaceae] (Costa Rican guava) |
hawthorne | Crataegis spp. [Rosaceae] |
ironwood | Sideroxylon inerme |
jaboticaba | Myrciaria cauliflora (DC.) Berg. [Myrtaceae] |
jackfruit | Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. [Moraceae] |
jambu | Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels [Myrtaceae] |
Jerusalem cherry | Solanum pseudocapsicum L. [Solanaceae] |
kei apple | Dovyalis caffra (Hook.f. and Harv.] Warb. |
kiwifruit | Actinidia deliciosa (a. Chev.) Liang and Ferguson [Actinidiaceae] |
kumquat | Fortunella japonica (Thumb.) Swing.; *F.margarita (Lour.) Swing. [Rutaceae] |
lemon | Citrus limon x C. chinense[Rutaceae] |
lemon (Meyer) | Citrus meyeri Tanaka L [Rutaceae] |
loganberry | Rubus loganobaccus L. H. Bailey [Rosaceae] |
longan | Euphoria longan (Lour.) Stued. [Sapindaceae] |
loquat | Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindley [Rosaceae] |
Madagascar olive | Noronihia emarginata (Lam.) Thours ex Hook [Oleaceae] |
mamey sapote | Pouteria spanota (jacq.) H.E. Moore and Stearn [Sapotaceae] |
mandarin | Citrus reticulata Blanco [Rutaceae] |
mango | Mangifera indica L. [Anacardiaceae] |
mock orange | Murraya paniculata L. Jack [Rutaceae] M exotica |
mombin | Spondias spp. |
monstera | Monstera deliciosa Liebm. [Araceae] |
mountain apple (Malay apple) | Syzygium malaccensis L. Merrill and L.M. Perry [Myrtaceae] Eugenia |
mulberry | Morus nigra L. [Moraceae] |
nashi | Pyrus pyrifolia var. culta (Mak.) Nakai or P. betulaefolia[Rosaceae] |
natal plum | Carissa macrocarpa Terminalia chebula |
nectarine | Prunus persicae var. nectarina (R.Br.) Maxim. [Rosaceae] |
orange | Citrus aurantium L.; C. sinensis L, Osbeck [Rutaceae] |
otaheite apple | Spondias cytherea Sonn. [Anacardiaceae] |
peach | Prunus persicae L. Batsch [Rosaceae] |
pear | Pyrus communis L. [Rosaceae] |
pepino | Solanum muricatum Aiton [Solanaceae] |
persimmon | Diospyros kaki L.f. [Ebenaceae] (Japanese persimmon) D.decandra Lour. [Ebenaceae] (persimmon) |
plum | Prunus domestica [Rosaceae] (prune) Prunus insitita L. [Rosaceae] (damson plum) Prunus salicina[Rosaceae] (Japanese plum) |
pomegranate | Punica granatum |
pond apple | Annona glabra |
prickly pear | Opuntia ficus indica L. Miller [Cactaceae] or Opuntia stricta (Haw.) Haw |
pummelo | Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck [Rutaceae] |
quince | Cydonia oblonga Miller [Rosaceae] |
raspberry | Rubus idaeus L. [Rosaceae] |
rollinia | Rollinia deliciosa Safford [Annonaceae] |
rose apple | Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston [Myrtaceae] |
santol | Sandoricum indicum Cav. [Meliaceae] |
sapodilla | Manilkara zapota (L.) Van Royen [Sapotaceae] |
soursop | Annona muricata L. [Annonaceae] |
Spanish cherry | Mimusops elengi L. [Sapotaceae] |
Surinam cherry | Eugenia uniflora L. [Myrtaceae] |
sweetsop (sugar apple) | Annona squamosa L. [Annonaceae] |
tamarillo | Cyphomandra betacea (Cao) Sendtner [Solanaceae] |
tangelo | Citrus reticulata x C. paradisi[Rutaceae] |
tomato (pink and red type) | Lycopersicon lycopersicum (L.) Karst. ex Farw. [Solanaceae] |
tree tomato | Cyphomandra betacea (Cav.) Sendtn. [Solanaceae] |
tropical almond | Terminalia catappa L. [Combretaceae] |
walnut | Juglans regia L. [Juglandaceae] |
wax apple (rose apple) | Eugenia jambos L. [Myrtaceae] (L.) Alston |
wax jambu | Syzgium samarangense (Blume) Merrill and L.M. Perrt [Myrtaceae] |
Common name | Scientific name and author |
avocado | Persea americana Mill. [Lauraceae] |
babaco (ripe) | Carica pentagona Heilb [Caricaceae] |
banana | Musa spp. [Musaceae] |
lime | Citrus aurantiifolia (Christm.) Swing. [Rutaceae] (West Indian lime) C. latifolia[Rutaceae] (Tahitian lime) C. reticulata var. Austera Lyb. [Rutaceae] (Rangpur lime) |
papaya | Carica papaya L. [Caricaceae] |
Common name | Scientific name and author |
durian | Durio zibethinus Murray [Bombacaceae] |
lychee | Litchi chinensis Sonn. [Sapindaceae] |
mangosteen | Garcinia mangostana L. [Clusiaceae] |
passionfruit | Passiflora edulis f. edulis Sims [Passifloraceae] (purple passionfruit) P. edulis f. flavicarpa Sims [Passifloraceae] (yellow passionfruit) |
pomegranate | Punica granatum L. [Punicaceae] |
rambutan | Nephelium lappaceum L. [Sapindaceae] |
sch 9 om 2007 SL No. 185 s 12
1Far northern pest quarantine area
The far northern pest quarantine area consists of the area of Queensland, north of latitude 13º45' south.Latitude 13º45' south passes near Coen.
2Coen to Cardwell pest quarantine area
The Coen to Cardwell pest quarantine area consists of the area of Queensland—(a)south of latitude 13º45' south; and(b)north of latitude 18º19.7' south.Latitude 18º19.7' south passes near Cardwell.s 2 sub 2008 SL No. 142 s 3
2ACardwell to Townsville pest quarantine area
The Cardwell to Townsville pest quarantine area consists of the area of Queensland—(a)south of latitude 18º19.7' south; and(b)north of latitude 19º15' south.Latitude 19º15' south passes near Townsville.s 2A ins 2008 SL No. 142 s 3
3Townsville to Bowen-Collinsville pest quarantine area
The Townsville to Bowen-Collinsville pest quarantine area is the area within the following boundary—•from latitude 19º15' south where it intersects the border of Queensland and the Northern Territory to where latitude 19º15' south intersects the eastern boundary of the Great Barrier Reef Region•then along the eastern boundary of the Great Barrier Reef Region to where it intersects latitude 19º53' south;•to latitude 19º53' south, longitude 148º05' east•to latitude 20º12' south, longitude 147º55' east•to latitude 20º33' south, longitude 147º51' east•to where latitude 20º33' south intersects the border of Queensland and the Northern Territory•then along the border of Queensland and the Northern Territory to where it intersects latitude 19º15' south.•Latitude 19º15' south passes near Townsville.•Latitude 19º53' south, longitude 148º05' east is in the vicinity of Abbot Point.•Latitude 20º12' south, longitude 147º55' east is in the vicinity of Mt Aberdeen.•Latitude 20º33' south, longitude 147º51' east is in the vicinity of Collinsville.
4Bowen-Collinsville to Rockhampton pest quarantine area
The Bowen-Collinsville to Rockhampton pest quarantine area consists of the area of Queensland—(a)south of the southern boundary of the Townsville to Bowen-Collinsville pest quarantine area; and(b)north of latitude 23º27' south.Latitude 23º27' south passes near Rockhampton.
5Rockhampton to Howard pest quarantine area
The Rockhampton to Howard pest quarantine area consists of the area of Queensland—(a)south of latitude 23º27' south; and(b)north of latitude 25º18.7' south.Latitude 25º18.7' south passes near Howard.
6Howard to New South Wales border pest quarantine area
The Howard to New South Wales border pest quarantine area—(a)consists of the area of Queensland south of latitude 25º18.7' south; but(b)does not include the Woodford special pest quarantine area.
7Woodford special pest quarantine area
The Woodford special pest quarantine area is the area within the following boundary—•from latitude 26º50' south, longitude 152º53' east to latitude 26º50' south, longitude 152º34' east•to latitude 27º04' south, longitude 152º34' east•to latitude 27º04' south, longitude 152º53' east•to latitude 26º50' south, longitude 152º53' east.•Latitude 26º50' south, longitude 152º53' east is in the vicinity of Peachester.•Longitude 152º34' east passes near Kilcoy.•Latitude 27º04' south passes near Mount Mee.
section 113, definition sugarcane plant pest
leaf scald disease caused by Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowsonratoon stunting disease caused by Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli (Davies et al.) Evtushenko Sugarcane Fiji disease virus Sugarcane mosaic virus sugarcane striate mosaic associated virus (uncharacterised) Ustilago scitaminea Syd. (abbreviated name—sugarcane smut)
sch 11 amd 2007 SL No. 185 s 13; 2009 SL No. 149 s 7
section 127, definition targeted pest
Insects and mites
Common name | Scientific name and author |
Bactrocera atrisetosa | Bactrocera atrisetosa (Perkins) |
Bactrocera decipiens | Bactrocera decipiens (Drew) |
Bactrocera kirki | Bactrocera kirki (Froggatt) |
Bactrocera tau | Bactrocera tau (Walker) |
Bactrocera trilineola | Bactrocera trilineola Drew |
Bactrocera trivialis | Bactrocera trivialis (Drew) |
Bactrocera xanthodes | Bactrocera xanthodes (Broun) |
banana skipper | Erionota thrax (Linnaeus) |
banana stem weevil | Odoiporus longicollis (Oliver) |
Bezzi fruit fly | Bactrocera occipitalis (Bezzi) |
breadfruit fruit fly | Bactrocera umbrosa (Fabricius) |
Chinese fruit fly | Bactrocera minax (Enderlein) |
citrus blackfly | Aleurocanthus woglumi Ashby |
citrus fruit borer | Citripestis sagitiferella (Moore) |
citrus gall wasp | Bruchophagus muli (Boucek and Brough) |
citrus psylla or Asian citrus psylla | Diaphorina citri (Kuwayama) |
coffee mealybug | Planococcus lilacinus (Cockerell) |
Cook Islands fruit fly | Bactrocera melanotus (Coquillett) |
cut worm | Agrotis interjectionis (Guenée) |
Erythrina gall wasp | Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim |
Fijian fruit fly | Bactrocera passiflorae (Froggatt) |
guava fruit fly | Bactrocera correcta (Bezzi) |
Indian fruit fly | Bactrocera caryeae (Kapoor) |
Jack Beardsley mealybug | Pseudococcus jackbeardsleyi Gimpel & Miller |
Japanese citrus fruit fly | Bactrocera tsuneonis (Miyake) |
mango fruit borer | Citripestis eutraphera (Meyrick) |
mango leaf gall midge | Procontarinia spp. |
mango leafhopper | Idioscopus clypealis (Lethierry) |
mango leafhopper | Idioscopus nitidulus (=niveosparsus) (Walker) |
mango pulp weevil | Sternochetus frigidus (Fabricius) |
melon fly | Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) |
papaya fruit fly | Bactrocera papayae Drew and Hancock |
peach fruit fly | Bactrocera zonata (Saunders) |
Philippine fruit fly | Bactrocera philippinensis (Drew and Hancock) |
planthoppers | Perkinsiella spp. |
red banded mango caterpillar | Deanolis sublimbalis (Snellen) |
red imported fire ant | Solenopsis invicta (Buren) |
solanum fruit fly | Bactrocera latifrons (Hendel) |
spider mite | Tetranychus piercei McGregor |
Sri Lankan fruit fly | Bactrocera kandiensis Drew and Hancock |
stem borer | Chilo spp. |
sugarcane borer | Scirpophaga spp. |
sugarcane borer | Sesamia spp. |
sugarcane borer | Tetramoera schistanceana (Snellen) |
sugarcane leafhopper | Eumetopina spp. |
sugarcane leafhopper | Pyrilla perpusilla (Walker) |
sugarcane planthopper | Perkinsiella spp. |
sugarcane whitefly | Aleurodicus barodensis (Maskell) |
sugarcane woolly aphid | Ceratovacuna lanigera Zehntner |
Tongan fruit fly | Bactrocera facialis (Coquillett) |
vegetable leafminer | Liriomyza sativae Blanchard |
Molluscs
Common name | Scientific name and author |
giant African snail | Achatina fulica Bowditch |
A OrganismsBacteria“Liberobacter asiatica” Jagoueix et alPanotoea stewartii subsb. stewartii (E.F. Smith) Mergaert et al.“Pseudomonas celebensis”= banana blood disease bacterium (uncharacterised)Pseudomonas syzygii I. Roberts et al.Ralstonia solanacearum (E.F. Smith) Yabuuchi et al.Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) DowsonXanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri (Hasse) VauterinFungiClaviceps sorghi P. Kulkarni, Seshadri and HedgeCryphonectria cubensis (Bruner) HodgesElsinoe fawcettii Bitanc. and JenkinsFusarium oxysporum Schltdl. Fr. f. sp. cubense (E.F. Smith) W.C. Snyder and H.N. HansenHemileia vastatrix Berk. and BroomeMycosphaerella fijiensis M. Morelet (anamorph Paracercospora fijiensis (M. Morelet) Deighton)Peronosclerospora philippinensis (W. Weston) C.G. ShawPeronosclerospora sacchari (T. Miyake) Shirai and K. HaraPeronosclerospora sorghi (W. Weston and Uppal) C.G. ShawPhysopella ampelopsidis (Dietel and P. Syd.) Cummins and RamacharStagonospora sacchari T.T. Lo and Y. LingUstilago scitaminea Syd.
B Viruses and viroidsBanana bract mosaic virusBanana bunchy top virusCitrus tristeza virusCoconut cadang-cadang viroidPeanut stripe virusSorghum mosaic virusSugarcane Fiji disease virusSugarcane mosaic virussugarcane Ramu stunt virus (uncharacterised)Tomato leaf curl virus
sch 12 amd 2005 SL No. 332 s 6; 2007 SL No. 19 s 18; 2007 SL No. 258 s 5; 2008 SL No. 400 s 5; 2009 SL No. 149 s 8; 2011 SL No. 202 s 13; 2013 SL No. 141 s 4; 2016 SL No. 46 s 8
section 139(3), definition restricted plant
Acanthaceae
Agavaceae
Anacardiaceae
Apocynaceae
Aquifoliaceae
Araceae
Araliaceae
Asclepiadaceae
Cannaceae
Caprifoliaceae
Caricaceae
Convolvulaceae
Ebenaceae
Elaeocarpaceae
Euphorbiaceae
Fabaceae
Lauraceae
Lythraceae
Malpighiaceae
Malvaceae
Moraceae
Musaceae
Myricaceae
Myrtaceae
Oleaceae
Orchidaceae
Passifloraceae
Phyllanthaceae
Pittosporaceae
Punicaceae
Rubiaceae
Rutaceae
Saxifragaceae
Scrophulariaceae
Verbenaceae
sch 12A prev sch 12A ins 2004 SL No. 101 s 5
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 1 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 19
pres sch 12A ins 2016 SL No. 46 s 9
accredited business ...
def accredited business om 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(1)
affected area ...
def affected area ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(1)
affected area sign ...
def affected area sign ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(1)
Agvet Code ...
def Agvet Code ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(1)
approved condition see section 86.
approved disinfectant ...
def approved disinfectant ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
om 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(1)
approved disposal site ...
def approved disposal site om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
approved person ...
def approved person om 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
approved risk management plan, for chapter 3, part 2, see section 55 (2).
def approved risk management plan sub 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)–(2)
approved treatment method, for chapter 3, part 1, division 5, see section 28A (1).
def approved treatment method ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(5)
approved way means a way approved by the chief executive or an inspector.
Asian sugarcane planthopper, for chapter 3, part 12, see section 123.
def Asian sugarcane planthopper ins 2008 SL No. 17 s 5(2)
at any time, for chapter 3, part 18, see section 169.
def at any time ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 7(1)
authorised person—
(a)for chapter 3, part 3—see section 65; or
(b)for chapter 3, part 5—see section 75.
def authorised person amd 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(3)
sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
amd 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(3); 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(3)–(4); 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(2)
banana freckle, for chapter 3, part 1, see section 17.
def banana freckle ins 2013 SL No. 193 s 17(2)
banana leaf speckle pest means the banana leaf speckle disease caused by Mycosphaerella musae (Speg.) Syd. and P. Syd.
banana plant see section 17.
banana plant pest, for chapter 3, part 1, division 4, see section 25.
def banana plant pest sub 2013 SL No. 193 s 17
banana yellow Sigatoka pest means the banana yellow Sigatoka disease caused by Mycosphaerella musicola J.L. Mulder (anamorph Pseudocercospora musae (Zim.) Deighton).
branched broomrape see section 133.
def branched broomrape ins 2008 SL No. 134 s 5(1)
business person ...
def business person om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
canker ...
def canker ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
canker direction ...
def canker direction ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
Canker Notice ...
def Canker Notice ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
CGMMV, for chapter 3, part 18, see section 169.
def CGMMV ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 7(1)
citrus plant means a plant of the family Rutaceae.
See the Act, schedule 2, for the definition of plant.
def citrus plant ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
clarified juice see section 69.
clearance certificate ...
def clearance certificate om 2007 SL No. 185 s 14(1)
consumption movement ...
def consumption movement ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
destroy ...
def destroy ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
DPI fire ant approved symbol ...
def DPI fire ant approved symbol ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 20(2)
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
electric ant, for chapter 3, part 16, see section 153.
def electric ant ins 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
eligibility criteria provision ...
def eligibility criteria provision ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 4
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
eligible person ...
def eligible person ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 4
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
export movement ...
def export movement ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
far northern pest quarantine area—
(a)for chapter 3, part 1—see schedule 3, part 1; and
(b)for chapter 3, part 11—see schedule 10, section 1.
def far northern pest quarantine area amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch; 2009 SL No. 149 s 9(1)
filtered juice see section 69.
fire ant see section 38.
fire ant declaration ...
def fire ant declaration om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
fire blight area see section 65.
fresh juice see section 69.
fruit of a grape plant see section 69.
grape plant see section 69.
grape plant product see section 69.
Great Barrier Reef Region means the Great Barrier Reef Region under the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Act 1975 (Cwlth).
ground cover vegetation see section 17.
high risk item, for chapter 3, part 16, see section 154.
def high risk item sub 2003 SL No. 366 s 20(1)–(2); 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch; 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)–(2)
high risk restricted area, for chapter 3, part 2, see section 38.
def high risk restricted area ins 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(2)
host plant, for chapter 3, part 7, see section 86.
def host plant amd 2004 SL No. 101 s 6(1); 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(4)
sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
amd 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(3)–(4); 2007 SL No. 185 s 14(2)
sub 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)–(2)
infested plant, for chapter 3, part 18, see section 169.
def infested plant ins 2015 SL No. 5 s 7(1)
interstate department means the department of another State that deals with matters relating to agriculture in the State.
interstate inspector means a person who holds a position, however called, equivalent to an inspector, in an interstate department.
def interstate inspector sub 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)–(2)
interstate produce number ...
def interstate produce number ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
leaf scald disease means a disease of sugarcane caused by Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson.
local government area means a part of Queensland established as a local government area under the Local Government Act 1993 .
low risk restricted area, for chapter 3, part 2, see section 38.
def low risk restricted area ins 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(2)
mango leaf gall midge ...
def mango leaf gall midge ins 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(2)
om 2007 SL No. 258 s 6(1)
mango malformation disease, for chapter 3, part 17, see section 165.
def mango malformation disease ins 2008 SL No. 359 s 6(2)
mango plant—
(a)generally, means a plant of the genus Mangifera spp; or
(b)for chapter 3, part 17, see section 165.
def mango plant sub 2008 SL No. 359 s 6(1)–(2)
marc see section 69.
mill see the Sugar Industry Act 1999 , schedule.
def mill sub 2005 SL No. 332 s 7
must, for grapes, see section 69.
myrtle rust ...
def myrtle rust ins 2010 SL No. 339 s 7(1)
om 2011 SL No. 202 s 14(1)
native citrus plant ...
def native citrus plant ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
new fire ant colony ...
def new fire ant colony ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 4
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
nominated herbicide ...
def nominated herbicide ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
non-citrus plant ...
def non-citrus plant ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
non-quarantined area ...
def non-quarantined area ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
northern buffer pest quarantine area see schedule 3, part 2.
def northern buffer pest quarantine area amd 2009 SL No. 149 s 9(2)
northern pest quarantine area see schedule 3, part 3.
def northern pest quarantine area amd 2009 SL No. 149 s 9(2)
offence warning, for a requirement under this regulation, means a warning that it is an offence for the person to whom the requirement is given, or of whom it is made, not to comply with it.
def offence warning amd 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(5)
Ord Irrigation District ...
def Ord Irrigation District om 2007 SL No. 185 s 14(1)
other thing—
(a)for chapter 3, part 1, see section 17; or
(b)for chapter 3, part 4, see section 69.
def other thing prev def ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
pres def ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 24
sub 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(1), (5)
package includes a box, basket, case, container, crate, carton, cover or wrapper.
def package ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 20(2)
pest banana plant see section 17.
pest quarantine area—
(a)for chapter 3, part 1—see section 17; or
(b)for chapter 3, part 2—see section 38; or
(c)for chapter 3, part 3—see section 65; or
(d)for chapter 3, part 4—see section 69; or
(e)for chapter 3, part 5—see section 75; or
(f)for chapter 3, part 6—see section 82; or
(g)for chapter 3, part 7—see section 86; or
(h)for chapter 3, part 8—see section 91; or
(i)for chapter 3, part 9—see section 95; or
(j)for chapter 3, part 11—see section 113; or
(k)for chapter 3, part 12—see section 123; or
(l)for chapter 3, part 13—see section 127; or
(m)for chapter 3, part 14—see section 133; or
(n)for chapter 3, part 16—see section 153; or
(o)for chapter 3, part 17—see section 165; or
(p)for chapter 3, part 18—see section 169.
def pest quarantine area ins 2004 SL No. 101 s 6(2)
amd 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(6)
sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
amd 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(5)–(7); 2007 SL No. 185 s 14(3); 2007 SL No. 258 s 6(2)–(3); 2008 SL No. 17 s 5(3)–(4); 2008 SL No. 134 s 5(2); 2008 SL No. 359 s 6(3); 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(4); 2010 SL No. 339 s 7(2); 2011 SL No. 202 s 14(2); 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(3)–(4); 2015 SL No. 5 s 7(2)
pest site see section 25.
potato pest see section 95.
potato pest area see section 95.
potato plant means a plant of the species Solanum tuberosum L. (common name—potato).
def potato plant ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
prescribed cereal crop plant means each of the following—
(a)a plant of the species Secale cereale (common name—rye);
(b)a plant of the species Triticum aestivum (common name—wheat);
(c)a plant that is a hybrid of a plant mentioned in paragraph (a) and a plant mentioned in paragraph (b) (Tricitium X Secale).
def prescribed cereal crop plant ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
prescribed conditions ...
def prescribed conditions ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
prescribed matters ...
def prescribed matters ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
prescribed pest means a pest mentioned in schedule 1.
prescribed way ...
def prescribed way ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
property ...
def property ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 4
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
proposed risk management plan, for chapter 3, part 2, see section 56 (2) (a).
def proposed risk management plan ins 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(2)
pyriform scale see section 136.
ratoon stunting disease means a disease of sugarcane caused by Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli (Davies et al.) Evtushenko.
reasonably believes means to believe on grounds that are reasonable in the circumstances.
registered agricultural chemical product ...
def registered agricultural chemical product ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
registered agricultural marker dye means an agricultural marker dye registered by the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority.
At the commencement of this definition, the address of the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority’s website was <www.apvma.gov.au>.
def registered agricultural marker dye ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(5)
regulated fire blight host plant see section 65.
relevant business document ...
def relevant business document ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
relevant business movement ...
def relevant business movement ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
relevant host plant ...
def relevant host plant ins 2005 SL No. 157 s 6(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2009 SL No. 115 s 5(1)
restricted area—
(a)for chapter 3, part 2—see section 38; or
(b)for chapter 3, part 16—see section 153.
def restricted area sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
restricted item—
(a)for chapter 3, part 2—see section 38A; and
(b)for chapter 3, part 9—see section 95; and
(c)for chapter 3, part 18—see section 169.
def restricted item amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch; 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(5); 2015 SL No. 5 s 7(3)
reward amount ...
def reward amount ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 4
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
scheme ...
def scheme ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 4
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
scheme period ...
def scheme period ins 2008 SL No. 96 s 4
om 2012 SL No. 224 s 14(1)
show cause period see section 60 (1) (e).
soil—
(a)for chapter 3, part 2—see section 38; or
(b)for chapter 3, part 16—see section 153.
def soil ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 20(2)
sub 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
southern buffer pest quarantine area see schedule 3, part 4.
def southern buffer pest quarantine area amd 2009 SL No. 149 s 9(2)
southern pest quarantine area see schedule 3, part 6.
def southern pest quarantine area amd 2009 SL No. 149 s 9(2)
special pest quarantine area see schedule 3, part 5.
def special pest quarantine area amd 2009 SL No. 149 s 9(2)
stone fruit plant means a plant of the species Prunus spp.
def stone fruit plant ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
strawberry plant ...
def strawberry plant om 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(1)
strawberry plant pest ...
def strawberry plant pest om 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(1)
strawberry runner certification scheme ...
def strawberry runner certification scheme om 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(1)
strawberry runner scheme certificate ...
def strawberry runner scheme certificate om 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(1)
sugarcane Fiji disease means a disease of sugarcane caused by Sugarcane Fiji disease virus.
sugarcane mosaic disease means a disease of sugarcane caused by Sugarcane mosaic virus.
sugarcane plant means a plant of the genus Saccharum.
def sugarcane plant amd 2007 SL No. 185 s 14(4)
sub 2008 SL No. 17 s 5 (1)–(2)
sugarcane plant pest see section 113.
sugarcane striate mosaic disease means a disease of sugarcane caused by sugarcane striate mosaic associated virus (uncharacterised).
targeted pest see section 127.
treat, for chapter 3, part 2, see section 38.
def treat ins 2003 SL No. 366 s 20(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
treatment certificate see section 75.
treatment method A, for chapter 3, part 1, see schedule 5, item 1.
def treatment method A sub 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(1)–(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
sub 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)–(2)
treatment method A product ...
def treatment method A product ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
treatment method B, for chapter 3, part 1, see schedule 5, item 2.
def treatment method B sub 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(1)–(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
sub 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)–(2)
treatment method C, for chapter 3, part 1, see schedule 5, item 3.
def treatment method C sub 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(1)–(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
sub 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)–(2)
treatment method D, for chapter 3, part 1, see schedule 5, item 4.
def treatment method D sub 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(1)–(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
sub 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)–(2)
treatment method D product ...
def treatment method D product ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
treatment method E ...
def treatment method E ins 2004 SL No. 204 s 7(2)
amd 2006 SL No. 234 s 2 sch
om 2007 SL No. 19 s 20(1)
tropical race 4, for chapter 3, part 1, see section 17.
def tropical race 4 ins 2013 SL No. 32 s 24
vineyard soil, for chapter 3, part 4, see section 69.
def vineyard soil ins 2013 SL No. 80 s 22(5)
section 73 (2)
attachment 1 prev attachment 1 om 2008 SL No. 38 s 32
pres attachment 1 ins 2010 SL No. 119 s 7
sub 2013 SL No. 80 s 23
section 114 (2) and (3)
The map shows—•Far northern pest quarantine area
•Coen to Cardwell pest quarantine area
•Cardwell to Townsville pest quarantine area
•Townsville to Bowen-Collinsville pest quarantine area
•Bowen-Collinsville to Rockhampton pest quarantine area
•Rockhampton to Howard pest quarantine area
•Howard to New South Wales border pest quarantine area
•Woodford special pest quarantine area.
MAP
attachment 2 sub 2008 SL No. 142 s 4